AI for employee experience (EX) is transforming how organizations support their employees at work. By enabling more personalized work journeys, AI can improve engagement and overall EX. Research shows that AI-driven machine learning models can predict employee turnover with a high level of accuracy, with predictive performance scores above 0.8. This gives HR teams the opportunity to identify potential risks early and take action before issues lead to disengagement or exit. In addition, automation and real-time data are reshaping HR processes and helping employees work more efficiently.
This article explains how AI supports employee experience, covering common use cases, tools, benefits, and risks, and practical guidance for responsible adoption.
Contents
AI’s role in employee experience
AI for employee experience examples
AI for employee experience: Pros and cons
Top AI platforms for employee experience
9 ways to use AI to improve the employee experience
AIHR resources for HR professionals embracing AI
Key takeaways
- AI improves employee experience by reducing friction in everyday interactions and personalizing support across the employee life cycle.
- Automating high-volume, administrative tasks enables faster self-service for employees and frees up time for HR and managers to focus on higher-value work.
- Responsible use of AI is essential. Protecting employee data, addressing bias, and being transparent about how AI is used helps maintain trust.
- The most effective AI adoption starts with small, focused pilots and scales gradually as insights mature and links to experience and business outcomes become clearer.
AI’s role in employee experience
AI plays a practical role in shaping employee experience by using employee data such as feedback, interactions, and performance information to automate tasks and deliver more personalized support, communication, and learning. This helps reduce friction between employees, managers, and organizational processes, especially in areas where delays or generic responses tend to hurt the experience.
Across the employee life cycle, AI supports employees in several ways:
- Employee onboarding: Automatically creating role-based checklists and guiding new hires through their first weeks.
- Employee support: Routing HR and IT tickets and answering common questions to reduce response times.
- Learning and development: Personalizing course recommendations based on role, goals, and feedback.
- Wellbeing: Flagging high workloads and surfacing relevant employee assistance and wellbeing resources.
- Performance and communication: Drafting summaries, improving meeting efficiency, and tailoring internal messages by audience and tone.
As a result, AI can lead to faster access to information, fewer manual steps for employees and managers, more relevant learning opportunities, earlier identification of disengagement or turnover risks, and more consistent service through tools such as chatbots and smart ticket routing. At the same time, automation allows HR teams to shift their focus away from repetitive tasks and toward more complex employee needs, strategic priorities, and coaching.
AI for employee experience examples
AI is already being used across the employee life cycle to remove friction, personalize support, and improve everyday work experiences. Common examples include:
- Onboarding copilot: Streamlines the ramp-up process by creating personalized day-one agendas, assigning buddies, and flagging IT access needs by role, helping new hires feel supported and productive from the start.
- Policy Q&A chatbot: Provides accurate, 24/7 answers to HR and policy questions and escalates only complex cases to human specialists, reducing HR help desk volume and employee wait times.
- Skills-based learning paths: These use AI-driven skills assessments, career goals, and organizational needs to build targeted learning journeys, ensuring relevant and efficient employee development.
- Performance prep assistant: Drafts review summaries by pulling together goals, project notes, and 360-degree feedback, saving time and improving the quality of performance conversations.
- Manager 1:1 assistant: Compiles talking points for regular check-ins using data on workload, goal progress, and aggregated team sentiment, helping managers focus on support and development.
- Workload and wellbeing monitoring: Identifies potential burnout risks using signals such as scheduling patterns and workload data, then surfaces relevant wellbeing or employee assistance resources.
- Internal communication personalization: Tailors announcements and updates based on role, location, or team, reducing information overload and improving message relevance.
- Ticket routing and prioritization: Applies machine learning to assess urgency and required expertise for HR and IT requests, ensuring issues are assigned quickly to the right owner.
HR tip
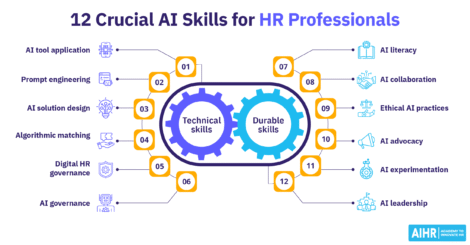
Successful application of AI for employee experience requires HR professionals to master three critical skills: prompt engineering (to optimize workflows), using generative AI in HR (a hands-on platform skill), and AI strategy for HR (plan for AI readiness). AIHR’s School of Artificial Intelligence for HR helps HR professionals build these skills and apply AI confidently in everyday HR work.
AI for employee experience: Pros and cons
If you’re considering using AI to improve employee experience, it’s important to weigh the efficiency gains against the potential risks. When applied thoughtfully, AI can remove friction and improve access to support. When applied poorly, it can undermine trust and create new challenges for HR teams.
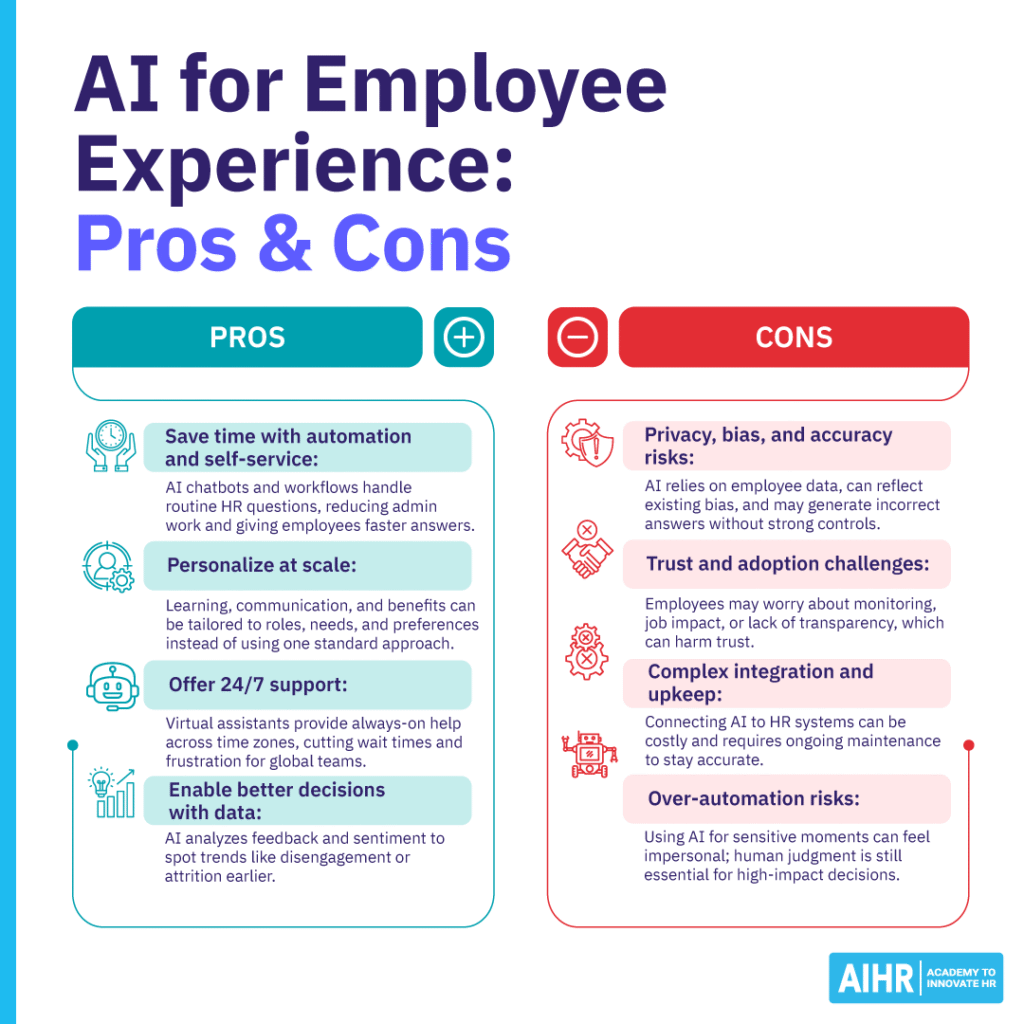
Pros
- Time savings through automation and self-service: AI-powered chatbots and robotic process automation can handle high-volume, routine questions, such as policy queries or basic HR requests. This reduces administrative workload for HR teams while giving employees faster, more consistent responses.
- Personalization at scale: AI makes it possible to tailor learning, communication, and benefits information to individual employees based on factors such as role, performance, and preferences. This helps move away from one-size-fits-all approaches and makes interactions feel more relevant and useful.
- Always-on support across time zones: Virtual assistants can provide 24/7 support, which is particularly valuable for global or hybrid workforces. Employees can get answers to urgent HR or IT questions almost immediately, reducing frustration and minimizing delays.
- More informed, data-driven decisions: By analyzing open-text feedback, surveys, and interaction data, AI can surface patterns and sentiment that are difficult to detect manually. These insights can help HR teams spot emerging risks, such as disengagement or attrition, earlier and respond more proactively.
Cons
- Data privacy concerns, bias, and hallucinations: AI use requires access to large volumes of employee data, which increases privacy and compliance risks if not managed carefully. AI models can also reflect existing bias in historical data, and generative tools may produce confident but inaccurate responses. Strong governance, controls, and ongoing monitoring are essential.
- Change resistance and trust concerns: Employees may be wary of AI, particularly if they fear job displacement, increased monitoring, or a lack of privacy. Insufficient transparency on how and why AI is used can erode trust and negatively affect EX rather than improve it.
- Integration and ongoing maintenance: Integrating AI tools with existing HR systems, such as HRIS or learning platforms, can be complex and costly. Non-native AI solutions also require ongoing maintenance to prevent model drift, where outputs become less accurate as organizational context changes over time.
- Risk of over-automation: Relying too heavily on AI for sensitive interactions, such as performance discussions or wellbeing support, can make the workplace feel impersonal. To avoid this, AI should support decision-making rather than replace it, with clear human oversight for high-impact situations.
Top AI platforms for employee experience
There’s no single ‘right’ platform for every organization, but a handful of AI-driven HR and employee experience platforms stand out because they automate routine work, deliver insights from people data, and help employees find the support they need quickly. These tools vary in focus, ranging from employee support and communication to analytics and lifecycle management, but all contribute to a smoother, more personalized employee experience when implemented well.
Employee experience and support platforms
These platforms are often the most visible form of employee experience technology. They help employees find answers fast, reduce manual helpdesk work, and make internal knowledge easier to use:
- ChangeEngine: Designed specifically for employee experience, this tool offers AI-powered knowledge discovery, personalized content, and support across common EX needs.
- Moveworks: An autonomous AI support engine that reduces every friction by resolving common HR and IT questions directly from Slack, Teams, web, or mobile interfaces.
- Aisera: This tool provides AI support across channels, with multilingual and omnichannel capability for large enterprise environments.
Communication and engagement
The platforms below help tailor internal communications, deliver timely updates, and connect distributed teams:
- Staffbase: Focused on internal communications with AI-assisted content delivery that reaches frontline, deskless, and hybrid workforces.
- LumApps: An AI-enhanced intranet that delivers personalized information streams and community engagement based on role and context.
Integrated HR and lifecycle platforms
Broader HR systems include AI features that touch many employee experience moments, from analytics to learning and talent management:
- Workday: A comprehensive HR suite with AI-powered analytics, workforce planning, and conversational tools that support talent management and experience workflows.
- SAP SuccessFactors / Oracle Cloud HCM: Enterprise HR systems that embed AI for predictive insights, engagement analytics, and workflow automation.
Specialized toolsets and helpers
These tools are narrower in scope than the ones mentioned above, but useful when paired with broader systems:
- AI-powered chat and knowledge bots such as Leena AI and Winslow help employees get instant answers to policy, benefits, and HR questions — especially when integrated with Slack, Teams, or intranets.
- Performance and feedback platforms like PerformYard automate review cycles and continuous feedback while keeping engagement top of mind.
Across these platforms, the common thread is that AI helps reduce repetitive work, surface intelligence from employee data, and tailor experiences to individual needs without forcing HR into purely administrative roles.
How to choose the right type of AI platform
The right AI platform for an organization largely depends on its size, workforce structure, and HR maturity. Organizations early in their EX journey often start with employee support platforms to quickly reduce response times and manual workload. Teams managing large or dispersed workforces may prioritize communication and engagement tools to improve reach and relevance.
More mature HR functions typically rely on integrated platforms that connect data across the employee life cycle, and may turn to specialized tools to address specific gaps once core systems are in place.
Learn to use AI for employee experience
To use AI ethically and efficiently to boost EX, you must start small, set clear metrics, secure data, keep humans in the loop, audit regularly, and train managers.
✅ Understand the different types of AI, including purposes and benefits
✅ Apply an AI adoption framework to transform workflows and processes
✅ Apply advanced prompting techniques and adapt to your role
✅ Learn best practices for using Gen AI safely, securely, and ethically
Learn at your own pace with the online Artificial Intelligence for HR Certificate Program.
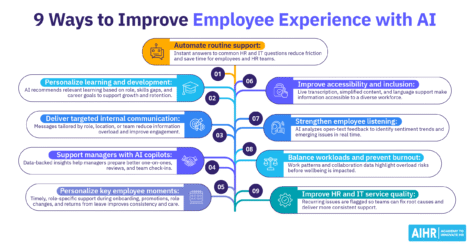
9 ways to use AI to improve the employee experience
Here are nine ways organizations are already using AI across onboarding, learning, communication, and people leadership to improve EX.
1. Automate routine support to reduce friction
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can handle high-volume, low-complexity requests such as policy questions, benefits lookups, and password resets. When issues are more complex, AI can automatically route HR or IT tickets to the relevant team, attaching the necessary context.
This reduces the need for employees to navigate multiple systems and allows HR teams to spend less time on repetitive tasks and more time supporting complex employee needs.
2. Personalize learning and development at scale
AI enables more relevant learning experiences by analyzing roles, skills gaps, performance data, and career goals. Based on this information, AI tools can recommend tailored learning paths, targeted microlearning, or reskilling opportunities aligned with both individual growth and business needs.
This approach moves employee development away from generic training catalogs and toward learning that supports career progression, engagement, and long-term retention.
3. Deliver more relevant internal communication
Generative AI can help HR and internal communications teams tailor announcements to different employee groups based on role, location, shift pattern, or function. Instead of sending the same message to everyone, AI helps ensure employees receive information that is relevant to them.
By refining their targeting and timing, organizations can reduce email fatigue, enhance message engagement, and clarify their policies, changes, and priorities.
4. Support managers with AI copilots
AI-powered manager copilots help line managers prepare for one-on-one conversations, performance discussions, and team check-ins. These tools can surface insights related to workload, goal progress, engagement signals, or emerging risks, helping managers focus conversations on support and development rather than administration.
Used responsibly, AI allows managers to identify potential issues earlier and shift their role from task coordination to coaching and people leadership.
5. Personalize key moments across the employee life cycle
AI helps HR teams deliver timely, personalized experiences during key moments, such as onboarding, promotions, role changes, relocations, or returns from leave. For example, AI can trigger role-specific onboarding checklists, recommend learning during a transition, or prompt managers to check in after a major life event.
Automating and personalizing these touchpoints helps employees feel supported and valued at critical stages of their journey.
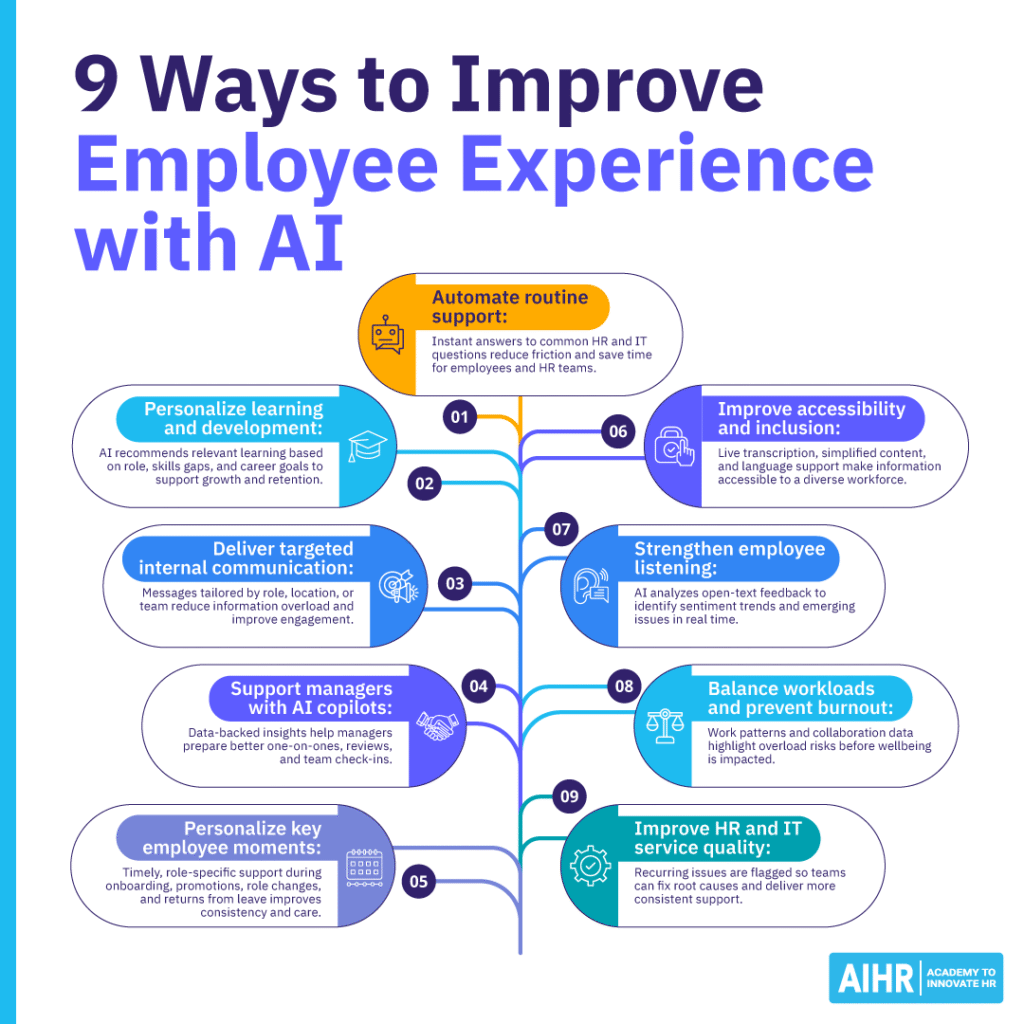
6. Improve accessibility and inclusion
AI can improve accessibility by providing live transcription for meetings, simplifying complex documentation, and supporting multiple languages across internal tools and platforms. This helps ensure information is accessible to employees with different needs, working styles, or language backgrounds.
By removing barriers to participation and understanding, AI supports more inclusive employee experiences and can positively influence engagement and retention.
7. Strengthen employee listening and feedback loops
AI can analyze large volumes of open-text feedback from surveys, pulse checks, and internal platforms to identify sentiment trends and recurring themes in real time. This goes beyond simple scores to capture how employees actually feel.
Continuous listening allows HR teams to respond faster to emerging issues, improve follow-through on feedback, and build greater trust by showing employees their voices are heard.
8. Improve workload balance and prevent burnout
AI can analyze signals such as meeting volume, overtime patterns, and task distribution to highlight uneven workloads across teams. These insights help managers spot risks before burnout becomes a problem.
When used responsibly, this supports healthier ways of working and enables earlier, data-informed interventions that protect wellbeing without relying solely on self-reporting.
9. Improve HR and IT service quality over time
Beyond ticket routing, AI can analyze service data to identify recurring issues that repeatedly disrupt employee experience, such as unclear policies or recurring technical problems. It can then suggest content updates or process improvements.
This helps HR and IT move from reactive support to proactive experience improvement, reducing repeat issues and improving service consistency for employees.
10 steps to implement AI for employee experience
When it comes to successful AI integration, change management and governance are just as important as the technology itself. Here’s a 10-step process using an AI benefits chatbot scenario that explains how to roll out AI to improve the employee experience:
Step 1: Pick one high-friction point for proof of concept
Start small so you don’t become overwhelmed. Choose one busy area, such as compensation and benefits, and focus solely on it. Next, list the most common questions, note what you will not cover, and record current response times so you can compare later.
Step 2: Define quantifiable success metrics
Agree on a few numbers that define success. This may include faster answers, more questions solved on the first try, fewer tickets, and high satisfaction scores. Set exact goals (for instance, 50% faster replies) and decide what happens if you manage to hit them several weeks in a row.
Step 3: Map all relevant data and system dependencies
Gather the official sources for your answers (e.g., HRIS, SharePoint, or benefits sites). Label what’s sensitive, decide who can access what, and make sure the bot always points to a specific source. Be sure to also keep the content updated to avoid stale or duplicate answers.
Step 4: Select a pilot tool for low-risk, high-volume workflow
Shortlist a few vendors that offer strong security and easy integrations, then test them using real employee questions. When you’re done, compare accuracy, speed, and source citation, and choose the one that works best with your existing HR tools and systems.
Step 5: Establish governance and privacy protocols
Only collect what you need, set retention limits, and control who can make changes to the content. At the same time, enable audit logs and clearly state the bot’s limits in the interface. You should also define how the system escalates sensitive topics to human employees.
Step 6: Build prompts, guardrails, and escalation rules
Instruct the bot to use plain language, cite its sources, and say, “I don’t know” when it’s unsure. Additionally, remember to create simple rules: for example, certain keywords or low confidence could trigger a handoff to HR. At the same time, keep reusable prompts and reply templates.
Step 7: Train internal champions and stakeholders
Thoroughly train HR Business Partners (HRBPs), managers, and your help desk team on how the AI works, and make them aware of its limitations. Also provide them with a quick-start guide and one place to submit fixes or new questions; they can then help others use it and spot issues early.
Step 8: Launch to a small cohort and collect feedback weekly
During your pilot, roll out the AI solution to HR to test it first, then to one business unit (e.g., Finance or Marketing) at a time. Implement a mechanism to collect qualitative feedback that includes EX and information accuracy ratings. Be sure to review this data on a weekly basis.
Step 9: Measure, analyze, and iterate continuously
Compare your pilot data against benchmark metrics to assess AI response accuracy ratings and employee satisfaction levels. If accuracy is low on a particular topic (e.g., 401(k) withdrawals), retrain your model immediately using more accurate source data.
Step 10: Scale to adjacent use cases and update policies
Once your benefits chatbot is stable, scale your knowledge base to handle additional areas, such as onboarding FAQs and personalized employee training. As your AI chatbot evolves, update your HR technology policies to reflect the wider use of GenAI in your organization.
HR tip
If you’re starting with AI and want quick, practical references you can use today, download AIHR’s AI in HR Cheat Sheet Collection for free. It breaks down key concepts, tools, prompts, and workflows into easy guides that help HR teams apply AI thoughtfully and effectively across common HR tasks.
AIHR resources for HR professionals embracing AI
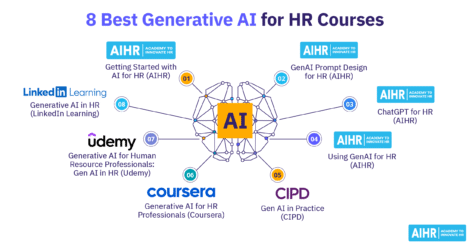
If you want to deepen your understanding of how AI is changing HR in practice, AIHR’s School of Artificial Intelligence for HR brings together a wide range of learning resources designed to help HR professionals apply AI responsibly and confidently. The School of AI includes 13 (mini) courses, the AI for HR Certification, an active AI community, live webinars, plus 11 on-demand recordings, and more than 25 templates and downloadable resources to support real HR use cases.
Together, these resources help HR professionals build practical AI skills, understand governance and risk, and apply AI to improve efficiency and the employee experience.
For ongoing learning, AIHR’s blog explores a wide range of practical AI use cases in HR, including:
- AI in HR: A Comprehensive Guide
- 47 HR AI Tools: The Ultimate List for HR Leaders
- AI in Performance Management: 11 Practical Applications To Guide You
Next steps
You don’t need to tackle everything at once. Start with one task you handle frequently, such as answering policy questions or drafting internal communications, and experiment with an AI tool you already feel comfortable using. Focus on keeping the scope small, and pay attention to where it saves time or reduces effort.
As your confidence grows, expand into slightly more complex use cases, such as analyzing survey feedback or creating tailored learning plans. Set a clear goal (e.g., reducing administrative work by 30%). Throughout this process, keep a few fundamentals in mind — protect sensitive employee data, review AI outputs before acting on them, and rely on human judgment for decisions that affect people directly. Used this way, AI supports your work without replacing your perspective or values.