Human Resources administration might sound simple, but it’s essential to managing your most valuable asset — your people. Unsurprisingly, technology is reshaping HR administration. For instance, the right software can reduce onboarding time by up to 80%, and the right payroll platform can save about 120 hours of admin work each month.
This article explores what Human Resources administration is, the role of an HR Administrator, HR Administrator jobs and best practices, and how to use AI in HR administration effectively and ethically.
Contents
What is Human Resources administration?
The role of an HR Administrator
Human Resources administration jobs
Human Resources administration: Best HR practices
What not to do in Human Resources administration (and why)
Ensure effective yet ethical AI use in HR administration
AI in HR administration: 5 practical rollout steps
Key takeaways
- Treat HR administration as critical ops — standardize with SOPs, automate routine work, validate and secure data, cross-train, and communicate clearly.
- Avoid HRIS update delays, don’t ignore retention rules, and don’t send PII over email without safeguards in place.
- Use AI for low-risk, high-volume tasks, like drafting comms, FAQs, checklists, data checks, simple reports, and ticket triage.
- Keep humans on binding decisions, protect PII with approved tools/DPAs, avoid AI for hiring/pay/discipline, audit for accuracy/bias, and stay transparent.
What is Human Resources administration?
Human Resources administration covers the day-to-day work that keeps HR running: maintaining and updating records, supporting recruitment and onboarding, managing benefits, and processing payroll. It also involves maintaining compliance with labor laws, protecting data, and providing clear communication and employee support.
Its goal is accuracy, consistency and efficiency, with repeatable processes that keep the organization running smoothly. HR administration also connects employees, managers, vendors, and HR systems. At the same time, it lowers the risk of fines and lawsuits, handles operational work, improves cost efficiency, and supports seamless EX.
The role of an HR Administrator
The role and responsibilities of an HR Administrator include:
- Maintaining accurate records: HR Admins must ensure employee records are accurate and up-to-date in the HRIS, including personal information, employment history, compensation and benefits enrollment, PTO and sick leave records, and regular audits.
- Preparing HR documents: These include offer letters, new contracts, policy memos, onboarding paperwork, and managing and updating templates.
- Coordinating employee onboarding and offboarding: This involves completing new-hire paperwork, I-9/E-Verify, orientations, and processing exit interview feedback.
- Supporting employee benefits administration: They must manage benefits enrollments, life events employees are navigating, and COBRA notices, as well as answer routine employee questions regarding benefits.
- Managing payroll: This entails liaising with the payroll team to collect and submit payroll inputs, including time changes, and deductions and status updates.
- Responding to inquiries: The HR Administrator is also responsible for answering basic employee and vendor inquiries, and directing more complex issues to the appropriate employee or department.
- Assisting in the recruitment process: This involves liaising with recruitment agencies, helping to organize recruitment events, setting up interviews, and preparing relevant correspondence with recruiters and candidates.
- Coordinating HR programs and initiatives: This covers learning and development programs, performance management, activities and initiatives to improve employee engagement, and research and data analysis.
- Prepare and manage HR communications: HR Administrators must develop HR policies and procedures, prepare announcement and memos, and ensure these are delivered to the right employees.
- Managing and coordinating HR calendars: Finally, they must schedule and organize meetings and appointments, take minutes during these meetings, and coordinate travel arrangements and training sessions.
Human Resources administration jobs
Below are some HR admin jobs and what they typically entail:
HR Administrator
An HR Administrator focuses on delivering broad, generalist administration services across all aspects of HR. These include employee records, onboarding and offboarding, benefits support, payroll inputs, compliance checklists and more to help the entire HR department run smoothly. They must also provide support for HR programs and initiatives to aid in their success.
HR Administrative Assistant
The HR Administrative Assistant is an entry-level role whose responsibilities involve providing general support to the HR team and HR Administrators. HR Admin Assistants do this by scheduling meetings, preparing relevant documents, maintaining files and records, and coordinating with applicants and candidates during the recruitment process.
HR Data Administrator
The HR Data Administrator is mainly responsible for documenting, organizing and retrieving data from HR systems. They focus on collecting, managing and analyzing employee data, maintaining an electronic filing system for electronic documents, using HR systems for accurate HR reporting, and maintaining and integrating the organization’s HR systems.
Benefits Administrator
The Benefits Administrator manages and oversees employee benefits packages, ensuring they can support the workforce’s personal and professional health. They are responsible for planning, assembling and updating each package. They must also communicate them to employees, guide them through enrollment, and help them make the most of their benefits.
Master Human Resources administration to boost your HR function
To optimize HR administration and boost your overall HR function, you must standardize processes, automate repeatable work, secure and audit data, measure performance, and communicate clearly.
✅ Master the HR processes that keep your organization running
✅ Create end-to-end HR processes, from recruitment to employee engagement
✅ Understand four common HR mistakes and how to prevent or correct them
✅ Use the three-brick model to strategically organize operations and long-term goals
Learn at your own pace with the online HR Generalist Certificate Program.
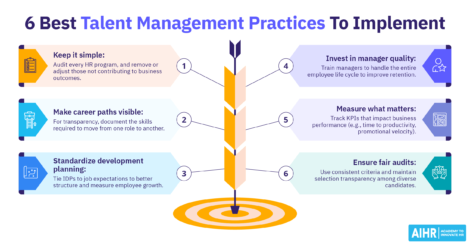
Human Resources administration: Best HR practices
To help you succeed in the HR Admin role, support employees, and ensure the organization meets its goals, here are some best HR practices to follow:
Use standardization to reduce errors
Create and follow clear checklists and standard operating procedures (SOPs) for every recurring task, such as onboarding, terminations, and payroll updates. Standardization cuts mistakes, shortens handovers, and makes quality measurable. It also gives new starters or stand-ins a reliable playbook, so work continues smoothly when people rotate or are out.
Automate repeatable tasks
Use HRIS features, workflow tools, and templates to automate requests, approvals, reminders, and document generation. HR automation speeds up routine work, reduces rework, and keeps processes consistent across teams and locations. The time you save can be redirected to higher-value tasks, like employee support and HR process improvement.
Validate data with routine audits
\Run scheduled audits to confirm names, tax IDs/SSNs, dependents, deductions, and employment status match across different systems. Catching errors early helps prevent payroll and benefits issues that can damage trust and lead to costly corrections. At the same time, keep a simple audit log that tracks what you checked, when you checked it, and what you fixed.
Secure data in line with privacy laws
To ensure data privacy and legal compliance, limit access based on role, encrypt data at rest and in transit, and follow clear retention and deletion rules. Additionally, align practices with relevant privacy laws and company policy to minimize legal and security risks. Be sure to also regularly review permissions, and archive or delete records you no longer need.

Document everything
Maintain clear records of changes, approvals, incidents, and employee performance and development. Consistent, detailed documentation supports key decisions — such as promotions or compensation changes — and provides audit trails when questions arise. Also use consistent file names and centralized storage, so records are easy to find.
Measure KPIs
Track response times for employee tickets, time to enroll for benefits, cycle times for common requests, and error rates in payroll and data entry. You can then use these metrics to spot bottlenecks and prioritize fixes that will have the biggest impact. Additionally, share simple HR dashboards, so leaders and partners can clearly view and track progress and risks.
Train backups and cross-train
Make sure more than one person can perform each HR administration task by training backups and cross-training team members. This will not only reduce single-point-of-failure risk, it will also keep HR operations running smoothly during vacations, illness, or peak periods. At the same time, keep quick-reference guides to ensure coverage is fast and consistent.
Communicate clearly with employees
Use plain, straightforward language, avoid obscure acronyms, and state exactly what employees need to do next, by when, and where they should go for help. Provide timelines, links to forms or portals, and examples when useful. Remember that clear, proactive communication reduces repeat questions and improves the employee experience.
What not to do in Human Resources administration (and why)
Here’s what to not to do in HR administration and why you should avoid making these mistakes:
Don’t rely solely on manual spreadsheets
Small businesses often use manual spreadsheets, as they’re familiar and affordable. But as the workforce grows, manual data entry and calculations can cause version drift and errors. For instance, Kodak experienced an Excel spreadsheet error that created an $11 million miscalculation. HR software can prevent this with automated calculations and standardized formats.
Don’t delay HRIS/payroll updates
Failing to update employee records can result in staff receiving incorrect pay and benefits, which can quickly lead to disgruntled employees and increase your organization’s legal risk. In addition, tax authorities can penalize companies for incorrect tax payments (due to payroll errors), and employees can file lawsuits for back pay, short pay, and non-payment.
Don’t ignore retention rules
Assess each data category and define what your organization needs to keep, the period it must keep it for (whether it’s statutory or internal policy), and how you’ll dispose of it when this period is over. Keeping data for too long can lead to liability issues, while disposing of data too early increases your organization’s risk of non-compliance.
Don’t send PII over email without safeguards
As far as possible, avoid sending personally identifiable information (PII) over email. But if you must, end-to-end encryption secures data during transmission. Alternatively, consider encrypted portals, secure file-sharing platforms and password-protected files that offer greater protection. All employees handling PII transmission should also undergo security awareness training.
Ensure effective yet ethical AI use in HR administration
AI can streamline HR admin and remove repetitive tasks, allowing you to focus on higher-value work. Practical uses include:
- Drafting routine communications (benefit reminders, new hire checklists)
- Turning policies and vendor docs into employee-friendly FAQs
- Generating checklists and SOPs from policies
- Running data quality checks (missing fields, mismatched dates, duplicates)
- Creating simple reports and dashboards from CSVs
- Triaging tickets by routing common questions to templates and escalating edge cases.
Chipotle is a good example of AI’s impact on HR administration: AI chatbots now handle the company’s initial candidate interactions, driving an 85% application completion rate and cutting time to hire from 12 days to four.
However, AI in HR also raises ethical and privacy risks, so it’s crucial to build in controls. Keep humans in the loop for decisions, approvals, and anything binding (policy, legal, compensation, benefits). You must also prioritize privacy — mask data where possible and never paste sensitive PII into AI tools without a signed DPA and an approved vendor.
Additionally, don’t use AI to make employment decisions, and be sure to involve diverse team members to spot issues. To enforce accuracy, use version control for prompts and outputs, and add a timestamp and owner to every AI-assisted document.
You must also be transparent with employees about where and how AI is used, its benefits, and its limits. Finally, codify your values, principles, and privacy rules in a clear AI policy, and implement an HR compliance strategy.
AI in HR administration: 5 practical rollout steps
Follow the five steps below to effectively incorporate AI into your Human Resources administration processes:
Step 1: Pick one workflow
Choose a single, narrow process — such as onboarding emails — and map the required steps, from trigger to completion. Identify where and how AI can draft content, route requests, or check data. Start small so you can test the AI quickly, measure its impact, and fix any issues before scaling it up and rolling it out across the entire organization.
Step 2: Create a prompt library and templates
Write clear, reusable prompts and templates tailored to the workflow you’ve selected (e.g., welcome emails, checklists, or FAQs). Include the purpose, audience, tone, required fields, and relevant examples. Then, make sure to store them centrally with version control, so anyone with access can generate consistent, on-brand outputs fast.
Step 3: Set approval rules and data handling standards
Define when AI can act automatically and when it requires human approval to move forward (e.g., policy changes, exceptions, or candidate correspondence). Provide structured inputs to ensure the model has the right context. Also set strict data rules — mask sensitive fields, restrict access, log usage, and use only approved tools with a signed DPA.
Step 4: Pilot your workflow within a small group
Train a small, motivated team on how to use the prompts, templates, and guardrails you’ve set up for your AI implementation. Then, run the pilot, capture feedback, and track issues in one place. Iterate on prompts and rules based on what works, what users find confusing, and where the process still requires manual steps.
Step 5: Measure the impact and expand with caution
Track time saved, error rates, turnaround times, and employee satisfaction metrics. Next, review outputs for bias and accuracy, and audit logs for compliance. If the results are promising, expand the AI rollout to the next workflow in phases. Throughout the process, prioritize human oversight, transparency, and legal compliance to ensure efficiency and minimize legal risk.
To sum up
Human Resources administration keeps your organization running. When you standardize processes, automate routine work, protect data, and measure results, you cut errors and free time for higher-value tasks. At the same time, strong documentation and clear communication build trust and make decisions easier to defend.
You can use AI to streamline low-risk workflows, but be sure to keep humans in control of decisions that affect people. Start small, use prompt libraries, set approval and data rules, pilot with a trained group, and track impact before you scale. Most importantly, stay transparent, audit regularly, and expand only when outputs are accurate, fair, and compliant.