AI in recruitment is becoming increasingly widespread, with 53% of companies using it today, compared to just 26% several years ago. With tools automating everything from applicant screening to job description writing, talent acquisition professionals can speed up and scale the hiring process to reach and attract even the most passive candidates.
However, it’s important to remember that if not designed or implemented correctly, AI can replicate outdated, inefficient recruitment practices or lead to bias in hiring.
This article guides you through practical AI applications across the hiring journey, using real-life AI in recruitment examples from companies that have successfully implemented them.
Contents
How to use AI in recruitment
10 real-life AI in recruitment examples
When AI gets it wrong: AI bias in recruitment examples
Key takeaways
- AI helps recruiters work smarter by automating routine tasks, enhancing the candidate journey, and providing data-backed insights for informed hiring decisions.
- Even the most advanced AI can’t replace human insight. Recruiters still play a key role in interpreting results, building relationships, and making fair hiring decisions.
- While you may not be able to completely erase bias, you can manage it with smart checks, like regular audits, diverse data sets, and a transparent recruitment policy.
- Teams that use AI responsibly benefit from faster hiring, greater consistency, and fairer decisions.
How to use AI in recruitment
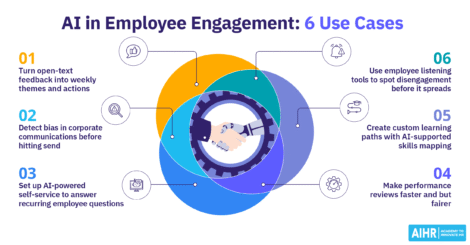
AI is changing how companies find and hire people. It helps recruiters work more efficiently, make fairer decisions, and focus on building stronger relationships with candidates, rather than performing repetitive tasks. Here are a few practical ways to use AI in recruitment:
- Sourcing talent: AI tools can scan job boards, LinkedIn, and internal databases to spot candidates who match your hiring requirements. It’s a faster way to find great talent, including passive candidates.
- Screening applications: Instead of reading through every résumé, recruiters can use algorithms to sort and rank applications based on skills, experience, and keywords. That means more time spent on interviews and less on admin work.
- Engaging candidates: Chatbots and automated messaging systems answer questions, schedule interviews, and send updates. This can enhance the candidate experience and reduce drop-off rates.
- Reducing bias: Well-designed AI systems can help identify biased language in job descriptions, suggest more inclusive terminology, and enable recruiters to focus on data rather than gut feel, resulting in fairer hiring decisions.
- Predicting success: Some platforms use predictive analytics in recruitment that can help identify which candidates are more likely to perform well in the roles they applied for, or stay with the company longer.
- Writing better job ads: Generative AI tools can assist in writing clear, detailed, and inclusive job descriptions that sound more attractive and can draw a wider range of talent to the company.
- Optimizing job ad placement: Algorithms can track which channels bring in the highest-quality applicants, and automatically shift ad budgets toward those that perform the best.
- Forecasting hiring needs: Predictive models can spot future workforce gaps by assessing turnover rates, growth trends, and market data. These details can help HR teams plan ahead, instead of reacting too late.
- Streamlining onboarding and compliance: AI chatbots can guide new hires through paperwork, training modules, and FAQs. Compliance tools can also automatically flag potential issues in job postings or offer letters, ensuring compliance with labor laws.
HR tip
Before scaling AI across the recruitment process, establish clear guidelines on fairness, transparency, and accountability. Define who reviews AI recommendations, how your team will audit results, and how the company protects candidate data. These rules ensure your use of AI in recruitment is in line with ethical and inclusive hiring practices.
10 real-life AI in recruitment examples
Here are 10 examples of companies that have been successfully using AI in recruitment, and the results they’ve seen so far:
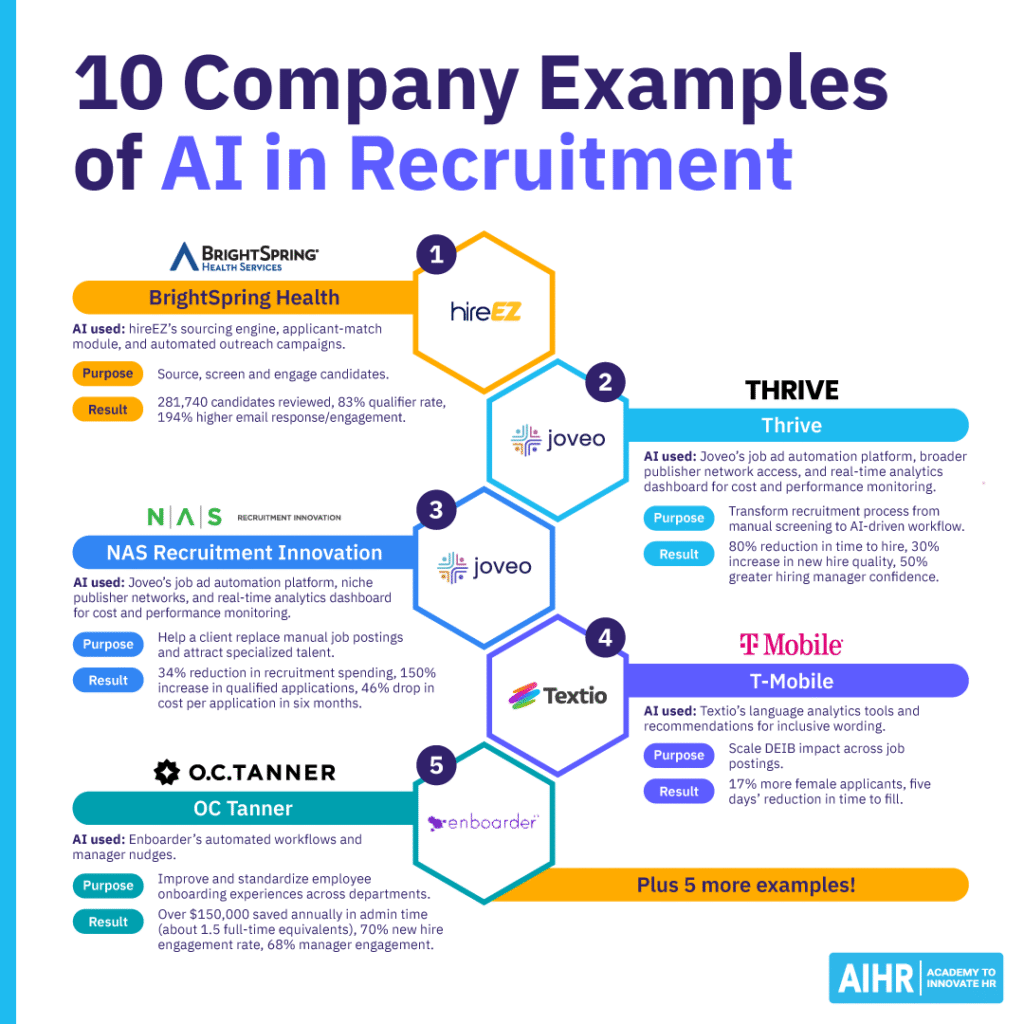
Example 1: BrightSpring Health
Healthcare company BrightSpring Health switched from relying primarily on Indeed and employee referral programs to using the AI-first platform hireEZ to source, screen, and engage candidates.
Tech used: hireEZ’s AI sourcing engine, applicant-match module, and automated outreach campaigns.
Results: BrightSpring Health has reviewed 281,740 candidates, achieved an 83% qualifier rate, and boosted email response/engagement by 194% through targeted AI-driven campaigns.
Example 2: Thrive
Career transition services firm Thrive partnered with AI-powered platform Ribbon.ai to transform its recruitment process, moving from manual screening to an AI-driven workflow.
Tech used: Ribbon’s AI tools for candidate screening, assessment automation, and structured interviews.
Results: An 80% reduction in time to hire, and a 30% increase in the quality of new hires. Thrive’s hiring managers also report 50% greater confidence in their decisions.
Example 3: NAS Recruitment Innovation
For a large animal welfare organization, recruitment marketing firm NAS Recruitment Innovation used AI-powered recruitment technology platform Joveo to help a large animal welfare organization replace manual job postings. Joveo also enabled the use of niche publisher networks to help the organization attract specialized talent (e.g., licensed veterinarians).
Tech used: Joveo’s job ad automation platform, broader publisher network access, and a real-time analytics dashboard for cost and performance monitoring.
Results: A 34% reduction in overall recruitment spending, 150% increase in qualified applications, and 46% drop in cost per application within six months.
Example 4: T‑Mobile
What they did: Mobile telecommunications company T-Mobile incorporated AI-driven writing platform Textio into its recruiting workflow to scale the impact of DEI (Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion) across its job postings.
Tech used: Textio’s language analytics tools and recommendations for inclusive wording.
Results: 17% more female applicants, and a reduction in time to fill of five days.
Example 5: OC Tanner
HR technology firm OC Tanner, which hires 200 to 300 new employees annually, faced disparate employee onboarding experiences across departments. To solve this problem, they turned to the AI software platform Enboarder.
Tech used: Enboarder’s automated workflows and manager nudges, which streamlined onboarding and standardized new hire journeys as early as two weeks before day one.
Results: Over $150,000 saved annually in admin time (about 1.5 full-time equivalents), 70% new hire engagement rate, and 68% manager engagement.
Become an AI‑savvy recruiter who’s irreplaceable
Writing job descriptions, screening resumes, and managing outreach doesn’t have to be manual anymore. The Artificial Intelligence for HR Certificate Program teaches you how to use GenAI tools to streamline your recruitment process and boost your impact.
✅ Design effective prompts for sourcing, screening, and candidate engagement
✅ Explore real-world GenAI applications in the hiring lifecycle
✅ Build a practical, ethical AI adoption plan tailored to your recruitment needs
Example 6: Walmart
American multinational retail corporation Walmart used skills-based assessments from AI hiring platform Vervoe to replace manual résumé screening for large-scale hiring (approximately 17,000 new associates a year).
Tech used: Video prompts, scenario-based tasks, and AI grading of candidate responses.
Results: 50% reduction in time to hire (14 to seven days), and attrition in retail operations dropped to single digits.
Example 7: Kimpton Hotels and Restaurants
Luxury boutique hotel chain Kimpton Hotels and Restaurants needed to process roughly 5,000 to 6,000 background checks per year. To make the process quicker and more efficient, they selected tech firm Checkr for its AI-driven background check services.
Tech used: Checkr’s AI-powered criminal background screening, analytics dashboard, and mobile-friendly candidate portal.
Results: A reduction in background check completion time from seven to 10 days to one day or less.
Example 8: AdvanceWorks
What they did: Technology services company AdvanceWorks partnered with AI recruitment services provider Manatal to revamp the former’s recruitment operations. This helped AdvanceWorks move from fragmented processes and siloed systems to an integrated, AI-enabled pipeline covering sourcing, tracking, and collaboration.
Tech used: Manatal’s multi-board job posting, automated candidate sourcing and ranking, and unified dashboard for feedback and collaboration.
Results: A 20% boost in recruitment team productivity (measured by interviews per week) and a 25% rise in positive candidate responses.
HR tip
While AI has transformed how recruiters find and evaluate talent, it hasn’t replaced human judgment — and most leaders don’t want it to. In fact, 93% of hiring managers say human involvement remains essential, as it can ensure fairness, empathy and context in every decision.
Example 9: Chipotle
American multinational restaurant chain Chipotle partnered with candidate experience AI agent Paradox to deploy a conversational AI assistant, Ava Cado. This assistant guided candidates through the application process, answered their questions, and scheduled interviews — all via mobile and chat.
Tech used: Paradox’s conversational hiring platform integrated with the company’s ATS (Workday), and a multilingual chatbot capable of engaging candidates in English, Spanish, French, and German.
Results: A 75% drop in average time from application to start date (12 days to four), and an increase in application completion rate from 50% to 85%.
Example 10: MM Group
During a major acquisition, global consumer packaging leader MM Group used Eightfold to integrate 3,500+ new employees across multiple sites and countries, and to streamline hiring with a unified AI-driven talent platform.
Tech used: A global talent intelligence platform launched across 22 sites, 11 countries, and in seven languages.
Results: A 42% decrease in time to hire, and an approximately 30% increase in applicant rate.
When AI gets it wrong: AI bias in recruitment examples
AI can make hiring faster and more efficient, but in some cases, it’s still prone to bias. Because these systems learn from past data, they can also inherit the same human biases present in such data. Below are some instances of how AI bias can show up in recruitment:
Gender bias in résumé screening
Gender bias happens when systems are mainly trained on data from one gender. This can lead the system to favor candidates whose profiles resemble those of that gender.
For example, Amazon’s AI recruiting tool was trained on résumés submitted mainly by men, leading the system to favor male-coded language (e.g., words like ‘executed’ or ‘captured’). It also penalized terms containing the word ‘women’, causing the company to downgrade female candidates for technical roles.
Age and racial bias in AI screening
AI tools can unintentionally discriminate by using patterns from past hiring data that correlate with age, race, or disability status. This can result in applications from older candidates or candidates of historically underrepresented backgrounds being filtered out before a human can review them.
A well-known case involved Workday’s AI-powered recruiting tools, which allegedly rejected candidates unfairly based on these factors. The EEOC later confirmed such tools fell under federal anti-discrimination laws.
Accent and language bias in AI interviews
AI tools used to analyze video or voice interviews can misinterpret speech patterns, accents, or pronunciation, resulting in lower scores for non-native English speakers or individuals with regional accents.
A recent University of Melbourne study found that AI interview systems made more transcription errors and less favorable assessments of non-native English speakers, highlighting how linguistic bias can impact fair evaluation.
Recency bias in résumé screening
Algorithms may prioritize recent activities or profile updates over long-term experience. If a candidate’s résumé has a newly listed HR certification or a recent project, the AI might rank them higher than an applicant with greater expertise.
In fact, a recent study by the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign highlighted that AI-driven résumé screeners can overvalue recent activities and keyword frequency, unintentionally disadvantaging candidates with extensive work histories or résumé gaps.
Similarity bias in skills matching
An AI system trained to value candidates with strong academic pedigrees or corporate experience is likely to overlook job seekers with transferable or non-traditional skills (e.g., freelancers, boot camp graduates, or small business professionals).
The Stanford Institute for Human-Centered AI echoed this sentiment, reporting that generative models tended to mirror the profile patterns of their training data — a phenomenon known as “homophily bias”.
Legacy bias from past hiring data
Predictive models that learn from historical hiring decisions can unintentionally continue old patterns of exclusion. If a company’s past hiring favored men for leadership roles, for instance, the AI will consider male applicants the ‘ideal hire’ and as such, exclude female applicants from managerial positions.
A Cornell University report confirmed that models trained on biased corporate data often replicate those same inequities, magnifying the gap and further limiting diversity over time.
Cultural bias in personality or behavioral tests
AI tools that measure ‘fit’ or communication style often reflect Western cultural norms. Candidates from collectivist cultures who avoid self-promotion might score lower on leadership or confidence traits, even if they perform well in team-based environments.
Paulo Rocha from the Centre for Intercultural Communication at Norway’s VID Specialized University highlights how cultural values shape the expression of personality traits across 22 countries. The paper also asserts that behavior-based assessments designed for Western norms might mis-score candidates from other cultures.
Referral and internal mobility bias
Some AI tools optimize referrals or internal mobility by learning from past successful promotions or placements. If those promotions favored specific groups (e.g., employees from certain departments or networks), the AI will replicate that pattern. This prioritizes existing networks over outside talent or underrepresented groups, hindering Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Belonging (DEIB) efforts.
HR tip
Before deploying AI in hiring, HR teams should actively monitor bias in algorithms. Research common types of bias and build in mechanisms to detect them early. When using tools like ChatGPT, frame prompts carefully (for example, ask for “ability to motivate teams” instead of “strong leadership qualities”) to encourage more accurate and fair outputs.
To sum up
AI in recruitment delivers the best results when clear guardrails are in place. The examples show faster hiring, better candidates and lower costs when teams define the problem, pick the right tool, and track impact.
Start small, prove value, then scale. Train hiring managers to use AI outputs, apply a simple risk checklist to every tool, and always keep humans in the loop. This way, you capture speed, consistency and a better candidate experience, all while keeping judgment and accountability with your team.
FAQ
AI helps recruiters automate time-consuming tasks, such as sourcing candidates, screening résumés, and scheduling interviews. It also provides insights to predict candidate success and improve the overall hiring experience.
Recruiters use AI for tasks like scanning job boards for talent, ranking applications, writing inclusive job descriptions, and matching candidates to open roles. Chatbots and virtual assistants are also common tools for engaging with candidates and answering their questions.
Leading employers like Unilever, IBM and Hilton use AI to streamline their hiring processes, from video interview analysis to predictive analytics that spot high-potential talent faster. Many smaller organizations are also adopting AI platforms to compete for top candidates more efficiently.
Yes, AI can reflect the same biases found in its training data. That’s why HR teams need to keep a close eye on algorithms, audit regularly, update data to remove bias, and make sure humans still have the final say.