AI in compliance helps you catch potential issues early, before they become real problems. It makes audits and policy reviews more efficient, saving time and money while reducing the risk of fines or legal action. For example, an AI system can automatically flag unusual transactions that might indicate fraud or policy breaches, allowing teams to investigate before regulators get involved.
This article dives into what AI in compliance is, how you can use AI to automate your compliance processes and shield your company against legal exposure, and which AI-powered tools you can use to help you along the way.
Contents
What is AI in compliance?
AI in compliance: Pros and cons
AI in compliance implementation: 4 key operational areas
7 top AI-powered regulatory compliance tools
The future of AI in compliance
How to ensure ethical use of AI in compliance
AIHR resources for HR professionals embracing AI
Key takeaways
- AI in compliance involves shifting from reactive auditing to proactive risk management by continuously monitoring and automating legal and policy adherence.
- A key benefit of AI in compliance is early, predictive risk detection and automation-driven administrative cost savings.
- However, HR must also establish strong governance measures to mitigate data security breaches and ethical risks, such as algorithmic bias.
- Integrating smart tools for audit-ready reporting requires strong human oversight to apply context, judgment, and ethical governance to tech-generated insights.
What is AI in compliance?
AI in compliance uses advanced software to monitor and improve legal and policy compliance. It turns compliance from reactive and manual into proactive and data-driven. This supports fair hiring practices, accurate payroll, unbiased performance reviews, and robust data privacy. Instead of reviewing thousands of records after a complaint, you receive timely alerts when risky data is detected.
Across the employee life cycle, AI can flag biased language in job ads and candidate data, wage and hour issues, misclassification risks, and overtime errors. It can also help HR monitor access, manage retention, and support compliance with GDPR and CCPA regulations.
Also, you can use it to analyze safety incidents to reveal patterns and training gaps, and confirm that required documentation (e.g., I-9s and policy acknowledgments) is complete, valid, and stored securely for audits.
AI in compliance: Pros and cons
Integrating AI into compliance can help optimize processes and lower costs, but it is essential to be aware of both the pros and cons. Here are some key advantages and disadvantages associated with AI in compliance:
Pros
- Automates repetitive checks and reporting: AI can quickly scan thousands of documents and data points for compliance markers, automating lengthy routine tasks like audit prep, policy version control, and mandatory reporting (e.g., EEO-1 reporting).
- Improves data accuracy and consistency: Since AI can consistently apply predefined rules across all employee data, it can eliminate the manual inconsistencies and errors that often plague human-driven documentation and payroll processes.
- Provides early risk detection with predictive insights: AI uses machine learning to analyze historical data and behavioral patterns to identify subtle trends (e.g., potential wage violations or policy adherence gaps) before they result in penalties or lawsuits.
- Saves time and reduces compliance costs: AI automation in HR drastically reduces operational costs associated with compliance administration, investigations, and remediation, and frees up your HR and legal teams to focus on strategic projects.
- Ensures continuous monitoring for HR and legal updates: Market-leading AI tools can track federal, state and local regulatory changes in real-time to provide automatic updates. This helps ensure your company is never caught off guard by new laws and regulations.
Cons
- Possible data bias or incorrect risk flags: If your underlying training data contains bias (e.g., favoring one demographic in past performance reviews), your AI may not flag or may even reinforce those biased outcomes. This creates, instead of mitigating risk.
- Privacy and security risks: AI in compliance can involve handling large volumes of highly sensitive employee data. If your security protocols fail, the potential for a massive data breach and regulatory fines is severe.
- Implementation and maintenance costs: Initial setup costs, integration with your existing HRIS, and ongoing licensing fees require a significant investment. This can make AI in compliance inaccessible for a smaller organization on a tight budget.
- Risk of overreliance on technology: Treating the AI output as gospel without involving human review is dangerous. With AI-driven compliance flags, HR must maintain a ‘human in the loop’ to assess context and apply judgment and ethical oversight.
- Need for ongoing monitoring and updates: AI models need continuous testing, retraining, and updates to remain effective and compliant. This creates a new, specialized maintenance workload you must factor into your HR function.
Master efficient, ethical AI use for compliance
To use AI ethically and efficiently to maintain compliance, you must learn how to set governance, protect data, monitor and audit models, train teams, and align use cases with laws and values.
AIHR’s Artificial Intelligence for HR Certificate Program will teach you:
✅ Understand the different types of AI, including purposes and benefits
✅ Apply an AI adoption framework to transform workflows and processes
✅ Apply advanced prompting techniques and adapt to your role
✅ Learn best practices for using Gen AI safely, securely, and ethically
AI in compliance implementation: 4 key operational areas
The secret to effective AI use for compliance is to focus on continuous and strategic risk management, instead of simply completing manual checklists. Concentrate on these four key operational areas:
1. Automate compliance assurance basics
- Key actions: Track document expirations and validity, automate payroll and tax compliance checks, and manage employee data privacy and access controls.
AI systems can automatically monitor essential compliance documents like professional certifications, government-mandated 1-9 forms, and necessary training records. Use AI to flag deadlines and initiate renewal requests without manual tracking automatically.
You can also implement AI tools that continuously audit your payroll against labor laws (e.g., minimum wage, overtime, and sick leave accruals) in real time and across multiple geographies. This can significantly reduce the risk of costly lawsuits or government penalties.
Additionally, use regulatory compliance tools to enforce strict data retention policies, monitor who accesses sensitive employee information, and ensure compliance with global frameworks such as GDPR, CCPA, and similar data privacy acts.
2. Shift to predictive risk prevention
- Key actions: Use predictive AI to identify areas of potential non-compliance, and send alerts to HR teams when potential issues arise.
Predictive models can analyze data patterns (e.g., unusual trends in leave requests that could indicate fatigue) to forecast exactly where overtime violations or unsafe scheduling practices are most likely to occur. One example is overly long shifts without sufficient rest breaks during high-demand periods.
You can also configure AI systems to deliver immediate contextual alerts in case of a compliance threshold breach (e.g., a manager approving too many consecutive shifts), or when data begins trending toward a risk area. This enables timely intervention before the issue becomes a violation.
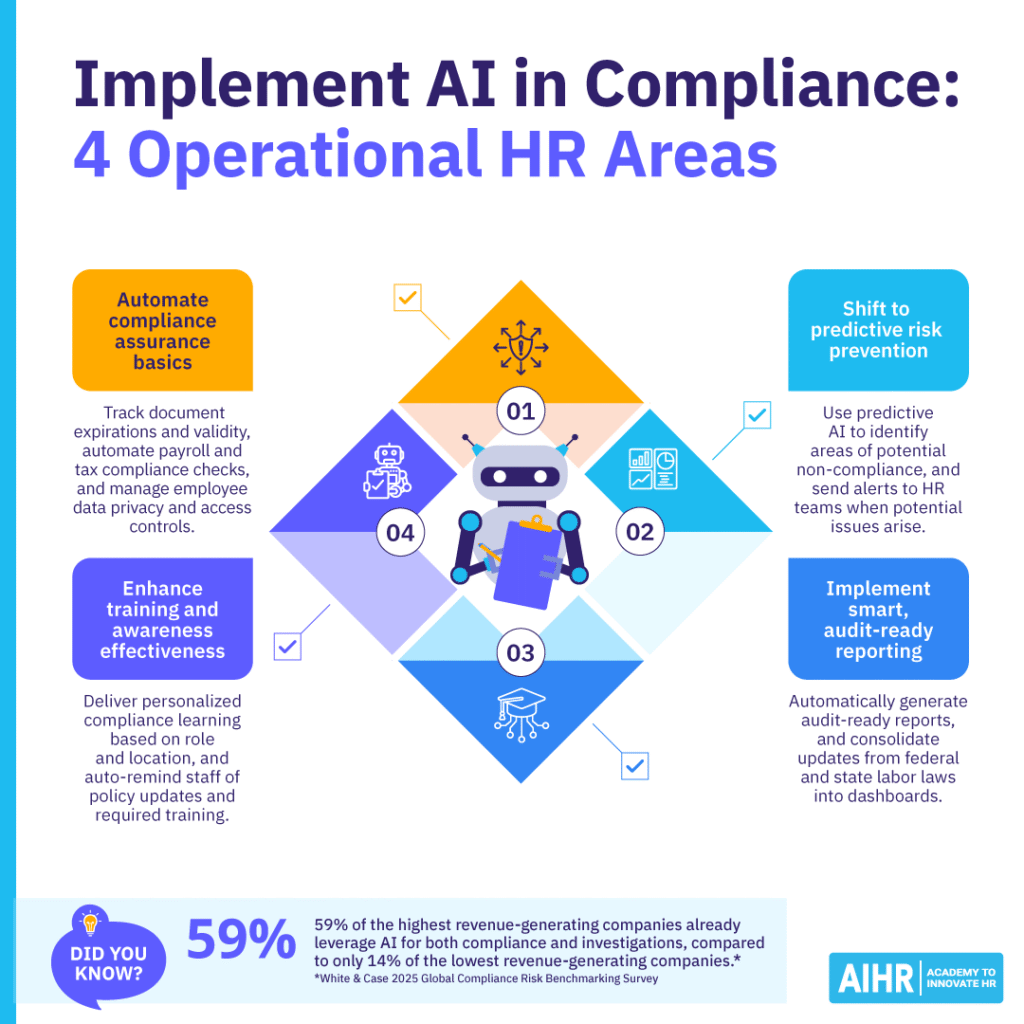
3. Implement smart, audit-ready reporting
- Key actions: Automatically generate audit-ready reports, and consolidate updates from federal and state labor laws into dashboards.
You can use AI to consolidate large amounts of employee data into structured, defensible, and legally sound compliance reports (including EEO-1, OFCCP audits, and wage summaries). This can help you avoid scrambling before an audit.
For quick executive reviews, AI can monitor legislative changes across multiple jurisdictions, translating legal jargon into actionable HR directives and displaying consolidated updates on centralized dashboards.
4. Enhance training and awareness effectiveness
- Key actions: Deliver personalized compliance learning based on role and location, and auto-remind staff of policy updates and required training
AI can analyze an employee’s job function, physical jurisdiction, and prior training history to assign only the necessary and most relevant compliance modules (e.g., California-specific sexual harassment training only for employees in California). This level of personalization can increase engagement and retention.
At the same time, you can use automated nudges and reminders to ensure your entire workforce acknowledges new policies and completes required annual training on time. This creates a complete, documented trail of compliance adherence across your team.
7 top AI-powered regulatory compliance tools
If your current HR tech stack doesn’t include strong AI regulatory compliance support, here’s a list of suitable tools and platforms to consider:
1. Workday People Analytics
Workday People Analytics uses AI to automate compliance monitoring, spot risks early, and keep data accurate. It scans payroll and workforce data for anomalies, predicts issues using sentiment, performance and history, and generates automated reports to minimize errors. Its integrated AI refines controls and ensures reliable reporting, while continuous updates support global privacy requirements such as GDPR.
2. ADP SmartCompliance
ADP SmartCompliance centralizes HCM compliance tasks and uses automated monitoring to flag potential errors early, so you can fulfill post-payroll obligations in areas like taxes and ACA. It aggregates data for real-time visibility, integrates with most payroll/ERP systems, and pairs technology with a network tracking federal, state and local rules in 11,000 jurisdictions — reducing manual work and improving audit readiness.
3. Trinet
Trinet features an AI-powered suite that embeds intelligent assistance in its HRIS to deliver policy guidance, faster answers, and data-driven flags. This suite can help SMBs anticipate compliance issues (e.g., classification or leave risks) while still maintaining strict privacy and security controls. As such, Trinet is able to support a more proactive, documented approach to regulatory compliance.
4. BambooHR
BambooHR offers VirgilHr, which uses AI to track federal, state and local labor laws and translate changes into clear, actionable guidance. An AI chatbot provides instant, tailored answers, while the system auto-generates multi-state-compliant handbooks and alerts HR to upcoming legal changes and deadlines. Side-by-side law comparison and automatic policy update prompts also help teams keep documentation current and avoid penalties.
5. ComplyAdvantage
ComplyAdvantage is an AI-driven financial crime risk solution that uses machine learning to screen for sanctions and adverse media in real time, cutting false positives by up to 70%. Its NLP ingests global news to keep risk data current, while AI-driven transaction monitoring reveals hidden risks. Automated workflows and integrations can also help maintain an auditable trail, helping you focus on true threats and scale compliance operations.
6. LogicGate Risk Cloud
LogicGate Risk Cloud is a dedicated Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) platform that streamlines AI-driven compliance with an AI Governance Solution for use case intake, policy, and risk management tied into broader GRC. AI auto-links risks, controls and policies, while an AI Text Assistant speeds up the drafting of tests and policies. Automated evidence collection also reduces manual work, and near real-time monitoring supports faster fixes.
7. Hyperproof
Hyperproof uses AI to automate evidence collection, map controls to regulations, and detect gaps and risks early, linking them to a central risk register for real-time monitoring. Its AI streamlines audits by auto-gathering proof and generating reports, supports continuous compliance with workflow triggers when issues appear, and powers the Mitigate module to track risk trends over time.
The future of AI in compliance
AI in compliance will push HR beyond basic automation toward connected, ethical risk management with proactive, predictive oversight. AI will move from reactive checks to forecasting risk, using analytics to spot patterns (e.g., wage and hour issues or bias in promotion paths) before they escalate.
These tools will be built into HR and compliance systems to monitor employee activity, data flows, and fast-changing global, federal, and local rules in real time. New regulations, including the EU AI Act, will also demand transparency, requiring companies to document how they use AI to help them make decisions in high-stakes areas like performance reviews and promotions.
HR leaders will need strong AI governance to ensure technology is effective, fair, and aligned with company values and employee rights. As an HR professional, you can achieve tighter collaboration among your company’s HR, legal, ris,k and IT teams to implement AI compliance organization-wide in a coordinated manner.
How to ensure ethical use of AI in compliance
HR leaders are responsible for mitigating the risks associated with AI in compliance, and must establish strong AI governance and ethical guardrails across all automated processes. Here’s how you can do it:
- Ensure transparency: Communicate clearly and proactively about where and how your company uses AI in its compliance processes, especially when the AI influences decisions related to hiring, promotion, or compensation.
- Establish consent and control: Make sure employees understand what data you use for compliance checks, and maintain strict human oversight and sign-off on all major decisions. The AI should inform, not dictate, outcomes like hiring or termination.
- Strengthen data privacy and security: Employee data is a main component of AI and compliance systems. Protect sensitive data with effective encryption, strict role-based access rules, and secure data retention policies.
- Conduct thorough bias checks: Regularly audit your AI’s outputs and algorithms for fairness and equity across different employee groups (e.g., gender, race, or age). This ensures your AI isn’t reinforcing historical biases present in your training data.
- Keep a human in the loop: Maintain human oversight in reviewing all AI-driven compliance flags and risk recommendations. This helps ensure the necessary context, judgment, and emotional intelligence AI lacks.
- Vendor due diligence: Select a solution provider with verifiable, third-party certifications (such as SOC 2 or ISO 27001) that prove responsible AI compliance, with strong controls over data protection, security, and operational compliance.
AIHR resources for HR professionals embracing AI
Certificate programs / online courses
The Artificial Intelligence for HR Certificate Program will help you build your knowledge and confidence in leading AI-driven digital transformations, and earn you Professional Development Credits (PDCs) to maintain any SHRM or HRCI accreditation you may already have.
Useful articles and resources
The following AIHR Blog articles can help increase your knowledge of AI’s applications in HR:
- AI in HR: A Comprehensive Guide
- AI and Automation in HR: Impact, Adoption and Future Outlook
- AI for Performance Reviews: Tools & Strategies for Smarter Talent Decisions
Next steps
Prioritize a focused pilot in a high-risk, high-volume area, such as overtime calculations or I-9 verification, and evaluate a managed AI compliance solution with clear success metrics. In parallel, an HR-Legal-IT working group should be set up to draft an AI governance framework that specifies transparency, data security, auditability, and escalation paths.
Next, build AI literacy across HR and Risk through reputable, HR-focused courses to strengthen internal expertise. At the same time, map and test a small set of end-to-end AI compliance use cases to assess feasibility and surface risks, validate controls, and inform a phased rollout plan.