HR technology has been transforming HR since the earliest computerized systems. Today, it’s an essential part of HR administration. This is why the global HR tech market continues to expand, with no signs of slowing. In fact, Fortune Business Insights projects it will grow from $47.32 billion this year to $95.95 billion in 2034.
This article highlights some of the many benefits of HR technology and shares examples and insights on how to make the most of it across the HR function.
Contents
What is HR technology?
The evolution of HR technology
7 examples of HR technology across the employee life cycle
Benefits and limitations of HR technology
7 steps to implement HR technology
Best practices for successfully using HR technology
HR technology trends
What is HR technology?
HR technology is a broad term for the software, hardware, tools, platforms, and applications that support and improve HR work across the employee life cycle, from hire to retire. Cloud platforms, AI, and data analytics, HR tech can automate processes, provide real-time decision-making insights, and support both employers and employees.
When used strategically, HR technology can reduce administrative work, strengthen data-driven decisions, improve the employee experience, and better align HR efforts with business goals.
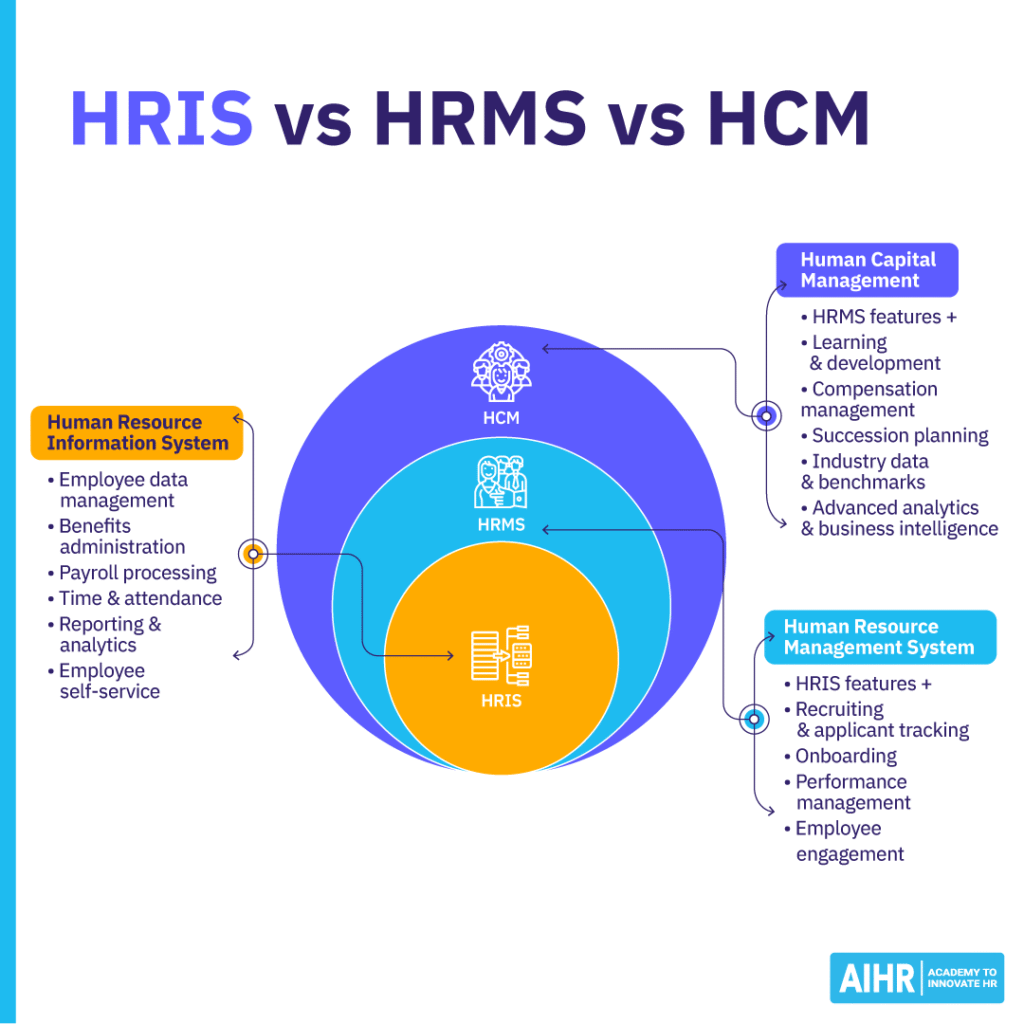
HR technology vs. HRIS vs. HRMS vs. HCM
Alongside “HR technology,” you’ll often hear terms like HRIS, HRMS, and HCM. Because vendors use these labels differently, it can get confusing. Here’s a simple way to think about it:
- HR technology is the umbrella term for all digital HR tools.
HRIS, HRMS, and HCM usually refer to core HR platforms that store employee data and support essential HR processes. In many organizations, this core platform acts as the “system of record,” but the exact features included vary by vendor.
The evolution of HR technology
HR technology looks and feels very different today than it did when it first emerged, or even compared to five to 10 years ago.
Several stages in its evolution have led us to where we are now:
- Early HR tech (1950s to 1970s): Focused on automating administrative work such as payroll, timekeeping, and recordkeeping.
- 1980s to 1990s: HR tech expanded as personal computers became more common and organizations adopted centralized HR software for recruiting, benefits administration, and performance management.
- 2000s to 2010s: A major shift occurred as cloud platforms and employee self-service portals became widespread, supporting more data-informed decisions and connected HR “stacks” of tools.
- 2020s: More advanced capabilities became mainstream, including predictive AI built into workflows, remote and hybrid work tools, virtual reality training in some settings, and more personalized employee experiences across the lifecycle.
Today, successful HR technology implementation is less about buying every available tool and more about making intentional choices that match organizational needs. That means building a coherent tech stack, maintaining clean and reliable data, and driving adoption so your HR technology investments actually deliver value.
Drive real value with HR technology (not just more tools)
Learn how to build a high-impact digital HR strategy, improve employee experience with design thinking, and automate HR processes to boost efficiency and reduce errors, while making sure adoption actually sticks.
With the Digital HR 2.0 Certificate Program, you will learn to:
✅ Benchmark your organization’s digital HR maturity and build a business case for digital transformation
✅ Map, optimize, and automate HR workflows using practical frameworks (and measure automation success)
✅ Lead digital change management to minimize resistance and drive long-term adoption
7 examples of HR technology across the employee life cycle
From recruitment to offboarding, HR technology can streamline work and improve the employee experience. Here are a few examples of HR tech solutions in action across the employee life cycle, along with sample providers:
Example 1: Recruitment
Recruitment platforms can optimize the hiring process. You can use them to post job ads, source candidates, schedule interviews, and screen applicants. This helps you identify qualified candidates faster, reduce manual work, and improve collaboration across the hiring team, leading to quicker, more informed hiring decisions.
Solution providers
Example 2: Onboarding
Onboarding technology helps organizations structure and automate the onboarding process, making it more efficient and engaging. Onboarding software can streamline paperwork and task assignments, reduce errors, support compliance, and help new hires get up to speed faster.
Solution providers
Example 3: Performance management
Performance management tools help track individual, team, and organizational performance so HR and managers can provide the right support. These tools can improve productivity by helping set and track goals, enabling ongoing feedback, and streamlining performance reviews.
They can also surface insights on performance trends and skills gaps to support data-informed decisions, helping employees grow and keeping work aligned with organizational objectives.
Solution providers
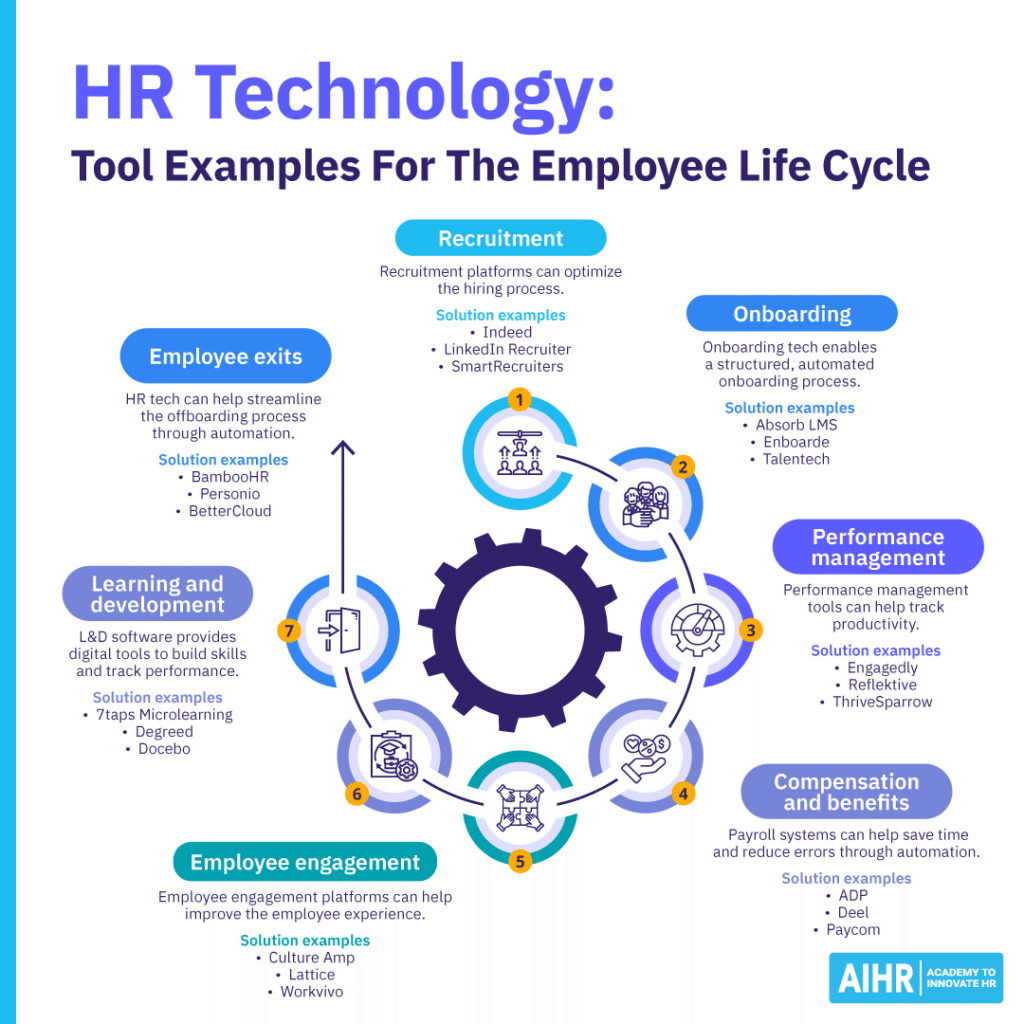
Example 4: Compensation and benefits
Payroll systems save time and reduce errors by automating payroll calculations, tax withholdings, and compliance tasks. They reduce administrative burden by supporting accurate, on-time pay, allowing HR teams to spend more time on higher-value work.
Many also provide centralized access to employee pay records, simplify reporting, and integrate with other HR tools such as time tracking and benefits administration. This improves efficiency, data accuracy, and decision-making.
Solution providers
Example 5: Employee engagement
Employee engagement platforms help improve the employee experience by facilitating better employee communication, gathering feedback, and recognizing achievements. With these tools, you can monitor employee sentiment through surveys and polls, identify issues early, and implement targeted initiatives to increase satisfaction and retention.
In addition, these platforms foster a sense of community through features like social feeds, collaboration tools, and peer recognition programs. By creating a more connected and supportive work environment, you can enhance morale, boost productivity, and align employee efforts with organizational goals.
Solution providers
Example 6: Learning and development (L&D)
L&D software supports employee training by providing digital tools to build skills, share knowledge, and track performance. It offers personalized learning paths, on-demand courses, and interactive content to engage employees while ensuring compliance with industry standards.
These platforms integrate with HR systems to monitor progress, assess competencies, and identify skills gaps, facilitating data-driven decision-making. By making training accessible and scalable, L&D software boosts employee growth, productivity, and retention, aligning workforce capabilities with business goals.
Solution providers
Example 7: Employee exits
HR tech streamlines the offboarding process by automating administrative tasks and providing a smoother transition for the employer and employee. These tools manage exit documentation, revoke system access, and handle final payroll processing efficiently.
They also support knowledge transfer through structured handovers and exit interviews, capturing valuable feedback to improve future offboarding experiences. By standardizing processes and reducing manual work, HR tech minimizes risks, maintains security, protects employer branding, and fosters alumni engagement.
Solution providers
AI in HR technology
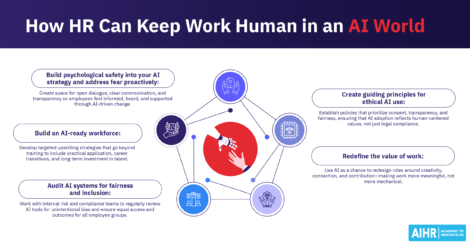
AI is now built into many HR platforms and specialized tools, supporting areas like recruiting, HR service delivery, learning, and analytics. HR teams use AI tools to draft and summarize content, automate workflows (like routing approvals or updating records), support employees and managers through self-service, and surface insights from HR data to spot patterns and trends.
At the same time, AI needs oversight. Bias risk and data privacy still apply, even when vendors make strong claims, so it’s important to have clear rules for when AI can be used, what data it can access, and how outputs are reviewed. In practice, this usually means documenting how the tool is used, training HR and managers on limitations, and keeping humans responsible for decisions that affect hiring, pay, performance, or employee relations.
Common AI use cases: Résumé screening and skills matching, chatbots for HR FAQs and case triage, personalized learning recommendations, drafting job descriptions or performance summaries, and predictive analytics (for example, turnover risk indicators).
Benefits and limitations of HR technology
HR technology offers advantages that help HR teams operate more efficiently. Key benefits include:
- Increased efficiency: Automating repetitive HR tasks reduces manual data entry in functions like payroll processing, benefits administration, and candidate screening, enabling faster workflows. Also, AI agents, predictive tools, and self-service portals free up HR teams to focus more on strategic initiatives.
- Improved decision-making: With access to centralized workforce information, real-time analytics and reporting, and AI-driven predictive insights, HR is better equipped to develop evidence-based strategies. AI can also support decisions by applying consistent criteria to tasks like candidate screening and workforce analysis, as long as outputs are monitored for fairness and accuracy.
- Better compliance and security: Built-in compliance features can support adherence to labor laws and data privacy requirements. This may include automated updates, deadline tracking, and training completion monitoring. Security features such as role-based access controls, encryption, and audit trails can reduce breach risk and support consistent reviews, including GDPR and CCPA-related requirements.
- Enhanced employee experience: User-friendly tools allow employees to access HR services and manage benefits when it’s convenient. Recognition platforms and real-time feedback tools can also support engagement by celebrating achievements and monitoring employee sentiment, which helps create a more connected and supportive work environment.
- Stronger talent management: Integrated HR AI technology solutions can support hiring, performance management, and employee development. For example, analytics can help identify potential leaders, inform development plans, and highlight skill gaps to support workforce planning.
With all that HR technology has to offer, it does have its shortcomings that are important to be aware of. Common limitations include:
- Integration challenges: Older systems may not integrate smoothly with newer tools. This can lead to manual workarounds, data silos, and inconsistent reporting, thereby limiting the effectiveness of HR tech.
- Implementation costs: Upfront expenses can be a barrier for smaller organizations. These costs include software, customization, and training.
- User adoption resistance: When employees and HR teams resist HR technology, it can lead to low usage and wasted investment. At the very least, implementation and adoption will take longer. Opposition can occur when employees fear their jobs are threatened, or the added effort needed to learn new systems seems overwhelming or pointless.
- Data quality and bias issues: Incomplete, inaccurate, or inconsistent data produce flawed metrics. If predictive tools are trained on biased data, AI analytics can generate compliance risks, inequitable hiring decisions, misguided strategies, etc. This undermines HR’s credibility.
- Insufficient for some HR functions: Certain HR functions are complex and require personal connection, which cannot be delegated to digital tools. Sensitive areas, such as conflict resolution, nuanced feedback, and employee relations issues, must be handled by human interaction.
HR tip
Embrace HR technology responsibly, especially when it comes to AI. Vet vendors carefully and run pilots to confirm privacy safeguards, data access controls, and clear accountability for how AI outputs are used.
7 steps to implement HR technology
A structured approach to implementing Human Resources technology ensures a smoother process. Consider following these seven steps:
Step 1: Assess your HR needs
The first step is to thoroughly assess your existing HR processes to identify pain points, inefficiencies, and bottlenecks that hinder HR operations. Gather feedback from the rest of your HR team, managers, and employees to understand their challenges and requirements. This ensures your HR tech investment aligns with company needs.
Step 2: Set clear objectives
Clearly define what you want to achieve with HR technology (e.g., automating payroll processing, improving recruitment efficiency, enhancing employee engagement, or ensuring compliance). Establishing well-defined objectives will help you select the right technology and measure its success once implemented.
Step 3: Choose the right technology
Research and evaluate different HR tech solutions. Consider cost, scalability, ease of use, integration capabilities, and vendor reputation. Also, compare software options, request demos, and check user reviews before deciding. The right technology should cater to the company’s needs and be flexible enough to accommodate future growth.
Develop a detailed project plan with timelines, budget, milestones, and risk mitigation. Evaluate vendors through demos, RFPs, and references to choose the right technology. Gather requirements via workshops to map current and future processes.
Step 4: Secure stakeholder buy-in
Getting support from key stakeholders (including leadership, HR teams, and employees) is crucial for successfully implementing HR tech. Present a clear business case highlighting the chosen technology’s benefits. Address potential concerns and demonstrate how the new system will improve HR processes without disrupting daily operations.
Step 5: Integrate with existing systems
Test functionality and ensure the HR technology tools you choose seamlessly integrate with your existing HR software and business systems. This will help you avoid data silos and ensure smooth workflow transitions. Work with IT teams and vendors to facilitate integration, minimize disruptions, and maintain data security throughout the process.
Step 6: Train HR teams and employees
Successful HR technology adoption depends on how well employees and HR teams understand and use it. Provide comprehensive training sessions, user guides, and resources to help everyone become familiar with the new system. Also, encourage hands-on practice and address any questions or concerns to build confidence in the effective use of HR tech.
Step 7: Monitor and optimize
Post-launch, continuously track the HR tech’s performance to evaluate whether it is still meeting your objectives. Collect user feedback, analyze key performance metrics, and identify areas for improvement. Regularly update and enhance the system to optimize processes and maximize the value of your HR tech investment.
HR tip
Roll out HR technology in stages based on priority and impact. For example, start with core HR and payroll, then move to recruiting and onboarding, and add performance tools or analytics in later phases.
Best practices for successfully using HR technology
If you want to make the most of HR technology, there are some best practices you can rely on. Here are three core concepts to keep in mind:
Start with an HR technology strategy
An HR technology strategy aligns HR processes and goals with HR tech solutions to improve efficiency, support organizational objectives, and drive innovation. This ensures technology in hr delivers the value your organization needs, namely efficiency gains and enhanced employee experience.
Creating this strategy should be your starting point. We’ve written a guide to help you develop your HR technology strategy, which you can refer to before you begin.
Prioritize training
Once you’ve established your HR tech strategy and started executing it, offer comprehensive training and support to everyone using the technology to help them become comfortable and proficient. Emphasize not only how to use the tech but also how it benefits users across teams and the organization itself. This applies to both your HR team members and employees outside of HR.
Plan for change management and adoption
Treat implementation like a change effort, not just a software rollout. Communicate early and clearly about what is changing and why, and provide simple support options like office hours, champions, and quick-start resources to help people adopt the new system.
Protect data quality and governance
HR technology depends on good data. Define ownership for key data sets, standardize definitions, and clean up records before migrating or integrating systems. This improves reporting accuracy, reduces confusion, and helps tools perform as expected.
Consider partnering with an HR tech consultant
With so many solutions on the market, it can be hard to stay current. If you need support selecting tools or designing your HR tech roadmap, an experienced consultant can bring specialist knowledge and help match solutions to organizational goals.
HR technology trends
New HR technology trends are building on AI’s established role in HR operations. Here’s a quick, slightly more detailed summary of 13 trends shaping HR tech right now:
- Trend 1: AI and machine learning in recruitment: AI is increasingly used to support sourcing, screening, interview scheduling, and candidate communication. The goal is faster hiring cycles and more consistent decisions, with strong oversight to reduce bias.
- Trend 2: Experience-driven HR service models: Self-service is becoming more personalized, with dashboards that bring together goals, benefits, pay information, and learning in one place. HR chatbots and guided workflows help employees get answers and complete tasks without waiting on HR.
- Trend 3: Employee experience platforms (EXPs): More organizations are using experience platforms to unify communications, resources, and day-to-day support. This makes it easier for employees to find what they need and helps HR keep messaging consistent across the workforce.
- Trend 4: Expanded use of predictive analytics: HR teams are using data to forecast workforce trends, not just report on what has already happened. Common use cases include identifying turnover risk, predicting hiring demand, and spotting early signals of engagement issues.
- Trend 5: Better integration with collaboration tools: HR tools are integrating more tightly with platforms like Microsoft Teams and Slack. This helps bring HR tasks into everyday workflows through approvals, reminders, and quick actions, which can improve adoption.
- Trend 6: AI-powered learning and development: Learning platforms are using AI to recommend training based on role requirements, skill gaps, and career goals. This supports more personalized learning paths and can make L&D easier to scale.
- Trend 7: Skills-based talent management: More organizations are organizing talent processes around skills rather than job titles alone. Skills data can support internal mobility, project staffing, succession planning, and more targeted upskilling.
- Trend 8: Employee listening and sentiment analysis: Pulse surveys and always-on feedback tools are growing, including better analysis of open-text comments. This helps HR spot patterns earlier and respond with more targeted actions.
- Trend 9: Well-being and mental health technology: Organizations are investing in tools that support well-being, resilience, and mental health. This often includes wellbeing apps, benefits navigation support, and access to coaching or counseling resources.
- Trend 10: Automation and AI agents for repetitive HR tasks: Automation is moving beyond basic workflows into more end-to-end support, such as coordinating onboarding steps, updating records, and prompting managers to complete tasks. The focus is on reducing manual effort while maintaining appropriate controls.
- Trend 11: SaaS and subscription-first HR technology: Cloud subscription models remain the default for many HR teams because they are easier to update, scale, and integrate. This also supports faster access to new features, including AI capabilities.
- Trend 12: Cybersecurity, privacy, and responsible AI: As HR data becomes more connected across systems, security and privacy expectations are rising. Organizations are strengthening access controls, audit trails, vendor due diligence, and responsible AI practices.
- Trend 13: Hybrid-ready, cloud-based HR ecosystems: HR tech continues to evolve to support hybrid and distributed teams. This includes remote onboarding, digital document management, virtual training, and tools designed for deskless workers.

To sum up
HR technology is a transformative force that delivers unmatched advantages by streamlining tasks, generating predictive insights, and elevating employee experiences. Leading with an HR tech strategy and following proven implementation steps and best practices positions HR to maximize HR technology and be a driving force behind business success.