The right leadership competency model can shape your top performers into future leaders who inspire teams, drive performance, and help the organization reach its wider goals. Great managers have some common traits, including open communication, motivating and engaging employees, and facilitating accountability.
However, 52% of employees said the main reason they’d quit their jobs was that they didn’t feel their managers valued them. This suggests that a lack of competent leaders can lead to companies losing talent. This article discusses leadership competencies and how to develop and implement a leadership competency model to nurture effective leadership.
Contents
What are leadership competencies?
What is a leadership competency model?
The purpose and importance of a leadership competency model
Types of leadership competency models
9 steps to develop a leadership competency model
7 real-world leadership competency model examples
What are leadership competencies?
Leadership competencies refer to the soft and technical skills, knowledge, behaviors, and other qualities that enable leaders to motivate and coach others to achieve shared strategic objectives. Different leadership roles usually require different leadership attributes and competencies, which leaders can achieve through competency mapping.
SHRM assigns key leadership competencies into three categories: competencies for leading the organization, competencies for leading others, and competencies for leading yourself. Some leadership core competencies include people management, decision-making, entrepreneurship, coaching ability, conflict management, and industry experience.
HR professionals must understand the key competencies of leaders so they can help develop effective leaders in their organizations.
What is a leadership competency model?
A leadership competency model, also known as a leadership competency framework, outlines the essential competencies leaders need within a specific industry or organization. Its development takes into account an organization’s goals, values, and leadership philosophy.
You can use it to identify, develop, and assess the performance of existing leaders and employees with leadership potential. This allows you to determine their suitability for leadership roles in the business.
The purpose and importance of a leadership competency model
An effective leadership competency model offers some important benefits to HR and employees, such as:
- Hiring and mobility: HR and managers can use the model to determine the right competencies for senior positions and candidates who possess them. This also helps in succession planning, as it identifies employees who could be potential successors.
- Training: A leadership competency model can help pinpoint skills gaps, allowing you to prioritize the most relevant training and development programs. Those interested in these roles will also be clear on their expectations and areas for improvement.
- Evaluation: The framework allows you to assess competencies and leadership performance. You can then target and measure skills, knowledge, and behaviors aligned with leadership and set clear expectations for those keen on leadership positions.
- Career planning: A leadership competency model can provide employees with a clear, detailed path to progression. This makes their career growth journey easier, which can boost motivation and performance and increase retention.
Types of leadership competency models
Here are some well-known, widely used leadership competency models you can consider for your organization:
SHRM Competency Model
The SHRM Competency Model is the result of research involving thousands of HR professionals to determine the nine most essential competencies for HR success.
These consist of eight behavioral competencies:
- Leadership and Navigation
- Ethical Practice
- Relationship Management
- Communication
- Global and Cultural Effectiveness
- Business Acumen
- Consultation
- Critical Evaluation
And one technical competency (HR expertise).
Korn Ferry Leadership Architect competency framework
The Korn Ferry Leadership Architect competency framework is a global competency framework that includes 38 behavioral leadership skills to help all employees make meaningful professional contributions.
The framework outlines the top competencies to look for based on the type of leader needed. For instance, a leader who excels at driving team engagement must be able to build effective teams, attract top talent, and provide vision and purpose.
Zenger Folkman Leadership Competency Model
The Zenger Folkman Leadership Competency Model is based on the concept of the “leadership tent,” which consists of five tent poles representing different sets of competencies: personal capability, a focus on results, character, interpersonal skills, and the ability to lead change.
These five poles cover a total of 19 competencies. According to the model, a person who masters only one of these poles is far less likely to succeed (8% to 9%) than someone who has mastered at least two poles (82%).
Drotter’s Leadership Pipeline Passages
Drotter’s Leadership Pipeline Passages is a well-known approach to leadership competency that provides a structure for understanding the expectations of leaders as they progress. It outlines six key transitions (or “passages”) leaders must navigate to grow within an organization. These passages involve shifts in skills, time application, and work values.
The transitions include moving from managing self to managing others and then managing managers. The next steps are functional leadership, business unit leadership, group leadership, and, finally, enterprise leadership. Each step requires new competencies, effective delegation, and embracing a broader perspective while letting go of previous operational roles.
Learn the skills you need to develop a successful leadership competency model
A good leadership competency model can help future-proof your organization by preparing potential leaders to fill crucial roles. To create the best model, you must define key competencies, identify skills gaps and leadership potential, and integrate them into your current systems.
In AIHR’s Talent Management and Succession Planning Certificate Program, you’ll learn to build an impactful leadership competency framework through skills-based talent mapping.
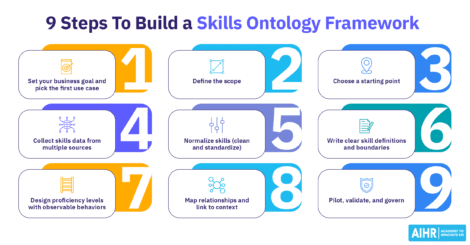
9 steps to develop a leadership competency model
To develop and implement an effective leadership competency model framework for your organization, follow these nine steps:
1. Understand organizational goals and culture
The first step to developing a leadership competency model is to carefully consider your organization’s objectives, values, mission, and culture. These will determine your needs and goals.
For example, assess your current leaders’ efficiency and pinpoint the missing or underdeveloped leadership skills preventing the company from reaching its goals. One-on-one interviews, focus groups, surveys, and performance data can help gather key insights.
2. Identify key leadership roles
The next step is to map out your leadership positions and determine their main responsibilities. This involves identifying the key tasks, decision-making authority, and areas of accountability for each role. Once you’ve established these responsibilities, you can develop a list of essential leadership competencies.
This approach ensures alignment between the expectations for each role and the skills and qualities required, helping create a solid foundation for effective leadership development and recruitment.
HR tip
Common leadership competencies include communication, team management, emotional intelligence, problem-solving, and innovation. The core competencies needed for your leaders to thrive may differ greatly from those needed in a different organization or industry. For example, the leadership competencies a software company needs would differ from those of a non-profit organization.
3. Engage stakeholders
It’s important to talk to key stakeholders (including directors, senior leaders, HR, managers, and employees) as early as possible to gain buy-in for your leadership framework. Show them how the proposed competency model will benefit them and the wider organization.
Additionally, engaging stakeholders promotes transparency and can help shape the overall design of your leadership competency model. It can also foster trust in the framework and your HR team.
4. Conduct competency research
Use industry benchmarks, alongside the models and best practices detailed in this article, to determine patterns of key or emerging leadership skills. Look for any competitive advantage you can find to develop and retain strong leaders.
You can also conduct a job analysis to review current leadership roles in your organization to spot any specific shared competencies that can help develop effective leaders.
5. Prioritize the most important competencies
By now, you’ll have an extensive list of key leadership competencies, which you should narrow down to seven to 10 core competencies. This is a manageable number for performance management, as well as training and development initiatives.
You can use a mix of surveys and performance data to validate your chosen competencies, learn how to adapt them to meet your organization’s needs, and prioritize them based on their impact on your workforce and the business.
Including leaders in the process of defining leadership competencies and desired behaviors is a great way to gain buy-in for your leadership competency model, and reinforce culture and values. And to integrate the model effectively into other practices and show organizational value, ensure it’s clearly defined and objectively measurable.

6. Establish behavioral indicators
Each competency must have defined tiers that provide a clear progression path for leaders (e.g., basic, intermediate, and expert levels). Additionally, each level needs a detailed description that clarifies the skills, knowledge, experience, and observable behaviors needed to perform at that level.
Include specific, measurable indicators for each competency level that demonstrate proficiency. This will help employees understand what’s expected of them and help managers conduct consistent performance evaluations across the organization.
7. Test and refine the model
The next step is to pilot your leadership competency model with a small group of leaders. Use a mix of feedback from focus groups, one-on-one interviews, workshops, and performance discussions to help inform any necessary changes.
This will also help drive buy-in and commitment to the model, allow you to adjust competencies if needed, and further align your framework with strategic organizational goals.
8. Integrate the model into your current HR processes
It’s important to train all leaders and your HR team on how to use the leadership competency model effectively. You can run workshops and create online resources to help leaders understand how to assess competencies, identify skills gaps, and create targeted development programs.
Integrate the model into key HR processes, such as hiring, training, performance evaluation, succession planning, and leadership development. Job descriptions, performance appraisals, and development plans should incorporate the chosen competencies to help employees pursue and achieve their career goals.
HR tip
Integrating your leadership competency model with HR processes helps to maximize its impact on organizational success. Integrating the leadership competency framework with HR processes such as recruitment, performance appraisals, and succession planning ensures consistency and maximizes its impact on organizational success.
9. Monitor and update the model whenever necessary
The final step is to set up a system that gives you continuous feedback on your leadership competency model so you can make improvements when needed. For example, sending a survey out three months after implementing the framework can help you determine if it’s helping develop effective leaders and if its competencies are relevant.
Remember that your leadership competency framework is an evolving system, and use regular feedback to help you make any required changes.

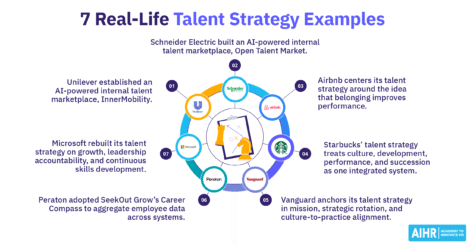
7 real-world leadership competency model examples
Here are some real-life examples of leadership competency models that could inspire your approach:
Example 1: California Department of Human Resources (CalHR)
The CalHR Leadership Competency Model includes the competencies of business acumen, inspirational leadership, results-oriented leadership, stewardship, talent management, and vision and strategic thinking.
Each broad competency covers a series of skills, knowledge, and behaviors. For example, inspirational leadership includes being mission-centric, actively engaged, and outcome-focused. Each smaller competency has proficiency-level behavior indicators, from level 1 (novice) to level 5 (expert).
Example 2: Deloitte
Deloitte’s Leadership Capability Model helps assess the potential of individual leaders. It has two distinct elements: developable capabilities (learned factors) and leadership potential (innate factors). The strength of a leader’s potential determines the speed of their progress in the organization.
Deloitte determined eight core competencies: inspirational leadership, execution, influence, collaboration, direction, business judgment, competitive edge, and talent-building. Each competency has four levels, from Operational Leader (level 1) to Enterprise Leader (level 4).
Example 3: GitLab
GitLab has a set of values, remote work, and functional competencies for each of its roles. It also uses a separate list of manager and leadership competencies in leadership development to create impactful training programs.
The company’s core leadership competencies are emotional intelligence, modeling a culture of feedback, coaching, conflict resolution, and building high-performing teams.
Example 4: KIPP
The KIPP leadership competency framework helps the organization effectively select, train, evaluate, retain, and promote leaders. The model’s main categories are Drive Results, Build Relationships, and Manage People, and these three categories contain core competencies.
For example, Drive Results includes achievement orientation, continuous learning, critical thinking and problem-solving, decision-making, and planning and execution. Each competency covers certain skills and behaviors. For instance, the key behaviors of achievement orientation are challenging goals, initiative, follow-through, resilience, flexibility, and focus on results.
Example 5: National Education Association (NEA)
The NEA Leadership Competency Model was created to define and assess education leaders’ leadership skills and abilities. It contains seven core competencies split into three categories or levels.
For instance, Level 1 covers foundational competencies linked to the leading of self; these competencies include organizing and strategy fiscal health. Level 2 covers mobilizing and power-building competencies associated with leading others, and Level 3 covers agenda-driving competencies needed to lead an organization.
Example 6: Procter & Gamble (P&G)
P&G uses the 5E Leadership Model, which revolves around five key actions: envisioning a clear future, engaging others in a shared purpose, enabling success through resources and support, executing plans with focus, and evaluating outcomes for continuous improvement.
This framework encourages leaders to align goals, foster collaboration, and adapt based on results to drive long-term success. Under this model, P&G identified three core competencies for success: leadership, strategy, and operational discipline. The company believes these are necessary to achieve personal and organizational goals.
Example 7: TATA Power
TATA Power’s transition to a green future has meant reskilling and upskilling its employees. To shape future leaders, its Aspire-Motivate-Perform (AMP) Leadership Competency Model takes a three-tiered approach to training.
The model emphasizes six key attributes: being powerful and nimble, energizing customers, delivering desired results, fueling excellence, being powered by purpose, and fostering a culture of continuous learning. Partnering with various institutions, it has created programs for senior leaders, middle management, and first-time managers.
To sum up
A leadership competency model helps build strong leaders who drive team success and keep your organization competitive. It provides clear guidance for hiring, training, and planning for the future, ensuring you prepare leaders sufficiently for future plans and challenges.
Investing in leadership development strengthens your team, improves engagement, and boosts overall performance. Take time to design the right leadership framework to support your leaders, integrate it into the organization, and monitor and refine it as the organization’s goals evolve.